Difference of coagulation features between severe pneumonia induced by SARS-CoV2 and non-SARS-CoV2
- PMID: 32246317
- PMCID: PMC7124128
- DOI: 10.1007/s11239-020-02105-8
Difference of coagulation features between severe pneumonia induced by SARS-CoV2 and non-SARS-CoV2
Abstract
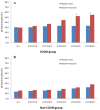
Severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is commonly complicated with coagulopathy, the difference of coagulation features between severe pneumonia induced by SARS-CoV2 and non-SARS-CoV2 has not been analyzed. Coagulation results and clinical features of consecutive patients with severe pneumonia induced by SARS-CoV2 (COVID group) and non-SARS-CoV2 (non-COVID group) in Tongji hospital were retrospectively analyzed and compared. Whether patients with elevated D-dimer could benefit from anticoagulant treatment was evaluated. There were 449 COVID patients and 104 non-COVID patients enrolled into the study. The 28-day mortality in COVID group was approximately twofold of mortality in non-COVID group (29.8% vs. 15.4%, P = 0.003), COVID group were older (65.1 ± 12.0 vs. 58.4 ± 18.0, years, P < 0.001) and with higher platelet count (215 ± 100 vs. 188 ± 98, ×109/L, P = 0.015), comparing to non-COVID group. The 28-day mortality of heparin users were lower than nonusers In COVID group with D-dimer > 3.0 μg/mL (32.8% vs. 52.4%, P = 0.017). Patients with severe pneumonia induced by SARS-CoV2 had higher platelet count than those induced by non-SARS-CoV2, and only the former with markedly elevated D-dimer may benefit from anticoagulant treatment.
Keywords: Coagulopathy; Coronavirus disease 2019; D-dimer; Severe pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Difference of coagulation features between severe pneumonia induced by SARS-CoV2 and non-SARS-CoV2.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021 May;51(4):1111-1112. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02115-6. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021. PMID: 33057907 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

