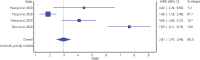
D-dimer is Associated with Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Pooled Analysis
- PMID: 32246450
- PMCID: PMC7295300
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1709650
D-dimer is Associated with Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Pooled Analysis
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Comment on
-
Laboratory abnormalities in patients with COVID-2019 infection.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020 Jun 25;58(7):1131-1134. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0198. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32119647 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization.Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 43Available at:https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed March 4, 2020
-
- Lippi G, Favaloro E J. Laboratory hemostasis: from biology to the bench. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2018;56(07):1035–1045. - PubMed
-
- Lippi G, Plebani M.Laboratory abnormalities in patients with COVID-2019 infectionClin Chem Lab Med2020. Doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0198 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical