Green tea catechins inhibit microglial activation which prevents the development of neurological disorders
- PMID: 32246619
- PMCID: PMC7513986
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.280300
Green tea catechins inhibit microglial activation which prevents the development of neurological disorders
Abstract
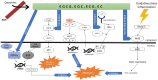
The over-activated microglial cells induce neuroinflammation which has the main role in neurological disorders. The over-activated microglia can disturb neuronal function by releasing inflammatory mediators leading to neuronal dysfunctions and death. Thus, inhibition of over-activated microglia may be an effective therapeutic approach for modulating neuroinflammation. Experimental studies have indicated anti-neuroinflammatory effects of flavonoids such as green tea catechins. The current research was aimed to review the effect of green tea catechins in inhibiting microglial cells, inflammatory cascades, and subsequent neurological diseases.
Keywords: catechins; green tea; microglia; neuroinflammation; neurological disease.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Green tea catechins: defensive role in cardiovascular disorders.Chin J Nat Med. 2013 Jul;11(4):345-53. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(13)60051-5. Chin J Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23845542 Review.
-
Wnt canonical pathway activator TWS119 drives microglial anti-inflammatory activation and facilitates neurological recovery following experimental stroke.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Dec 6;16(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1660-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31810470 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into the differences in anti-inflammatory activities of green tea catechins on IL-1β signaling in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Aug 15;329:112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.05.016. Epub 2017 May 19. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28532672 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid attenuates the inflammatory response by modulating microglia polarization through SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of the HMGB1/NF-κB pathway following experimental traumatic brain injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Apr 20;15(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1151-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29678169 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Effects of Green Tea Catechins in the Management of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2019;16(1):57-65. doi: 10.2174/1570163815666180219115453. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2019. PMID: 29468975 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Wasp Venom in BV-2 Microglial Cells in Comparison with Bee Venom.Insects. 2021 Mar 29;12(4):297. doi: 10.3390/insects12040297. Insects. 2021. PMID: 33805372 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of dietary polyphenols on neuroinflammation-associated disorders.Neurol Sci. 2021 Aug;42(8):3101-3119. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05303-1. Epub 2021 May 14. Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33988799 Review.
-
Tacca chantrieri André Rhizome Extract Alleviates Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Neuroinflammation in Rats.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2025 May 26;2025:7334303. doi: 10.1155/adpp/7334303. eCollection 2025. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40458441 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Flavonoids Against Mitochondriopathies and Associated Pathologies: Focus on the Predictive Approach and Personalized Prevention.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 11;22(16):8649. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168649. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Merging the Multi-Target Effects of Phytochemicals in Neurodegeneration: From Oxidative Stress to Protein Aggregation and Inflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 20;9(10):1022. doi: 10.3390/antiox9101022. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33092300 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aktas O, Prozorovski T, Smorodchenko A, Savaskan NE, Lauster R, Kloetzel PM, Infante-Duarte C, Brocke S, Zipp F. Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate mediates T cellular NF-kappa B inhibition and exerts neuroprotection in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2004;173:5794–800. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

