High-density genetic variation maps reveal the correlation between asymmetric interspecific introgressions and improvement of agronomic traits in Upland and Pima cotton varieties developed in Xinjiang, China
- PMID: 32246786
- PMCID: PMC7496985
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.14760
High-density genetic variation maps reveal the correlation between asymmetric interspecific introgressions and improvement of agronomic traits in Upland and Pima cotton varieties developed in Xinjiang, China
Abstract
The two new world tetraploid cottons, Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense, are cultivated worldwide and are characterised by a high yield and superior fibre quality, respectively. Historical genetic introgression has been reported between them; however, the existence of introgression and its genetic effects on agronomic traits remain unclear with regard to independent breeding of G. hirsutum (Upland cotton) and G. barbadense (Pima cotton) elite cultivars. We collected 159 G. hirsutum and 70 G. barbadense cultivars developed in Xinjiang, China, along with 30 semi-wild accessions of G. hirsutum, to perform interspecific introgression tests, intraspecific selection analyses and genome-wide association studies (GWAS) with fibre quality and yield component traits in multiple environments. In total, we identified seven interspecific introgression events and 52 selective sweep loci in G. hirsutum, as well as 17 interspecific introgression events and 19 selective sweep loci in G. barbadense. Correlation tests between agronomic traits and introgressions showed that introgression loci were mutually beneficial for the improvement of fibre quality and yield traits in both species. In addition, the phenotypic effects of four interspecific introgression events could be detected by intraspecific GWAS, with Gb_INT13 significantly improving fibre yield in G. barbadense. The present study describes the landscape of genetic introgression and selection between the two species, and highlights the genetic effects of introgression among populations, which can be used for future improvement of fibre yield and quality in G. barbadense and G. hirsutum, respectively.
Keywords: Gossypium barbadense; Gossypium hirsutum; GWAS; fibre traits; genetic introgression; selection.
© 2020 The Authors. The Plant Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
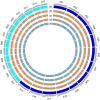

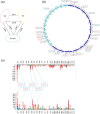

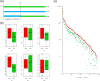
References
-
- Ai, H. , Fang, X. , Yang, B. et al (2015) Adaptation and possible ancient interspecies introgression in pigs identified by whole‐genome sequencing. Nat. Genet. 47, 217–225. - PubMed
-
- Akpertey, A. , Singh, R.J. , Diers, B.W. et al (2018) Genetic introgression from to soybean to increase seed yield. Crop Sci. 58, 1277.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

