Amygdala hyperreactivity to faces conditioned with a social-evaluative meaning- a multiplex, multigenerational fMRI study on social anxiety endophenotypes
- PMID: 32247196
- PMCID: PMC7125356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102247
Amygdala hyperreactivity to faces conditioned with a social-evaluative meaning- a multiplex, multigenerational fMRI study on social anxiety endophenotypes
Abstract
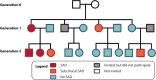
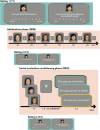
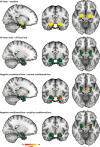
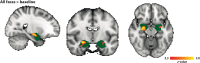
Social anxiety disorder (SAD) runs in families, but the neurobiological pathways underlying the genetic susceptibility towards SAD are largely unknown. Here, we employed an endophenotype approach, and tested the hypothesis that amygdala hyperreactivity to faces conditioned with a social-evaluative meaning is a candidate SAD endophenotype. We used data from the multiplex, multigenerational Leiden Family Lab study on Social Anxiety Disorder (eight families, n = 105) and investigated amygdala activation during a social-evaluative conditioning paradigm with high ecological validity in the context of SAD. Three neutral faces were repeatedly presented in combination with socially negative, positive or neutral sentences. We focused on two endophenotype criteria: co-segregation of the candidate endophenotype with the disorder within families, and heritability. Analyses of the fMRI data were restricted to the amygdala as a region of interest, and association analyses revealed that bilateral amygdala hyperreactivity in response to the conditioned faces co-segregated with social anxiety (SA; continuous measure) within the families; we found, however, no relationship between SA and brain activation in response to more specific fMRI contrasts. Furthermore, brain activation in a small subset of voxels within these amygdala clusters was at least moderately heritable. Taken together, these findings show that amygdala engagement in response to conditioned faces with a social-evaluative meaning qualifies as a neurobiological candidate endophenotype of social anxiety. Thereby, these data shed light on the genetic vulnerability to develop SAD.
Keywords: Amygdala; Endophenotypes; Functional magnetic resonance imaging; Social anxiety disorder.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impaired neural habituation to neutral faces in families genetically enriched for social anxiety disorder.Depress Anxiety. 2019 Dec;36(12):1143-1153. doi: 10.1002/da.22962. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Depress Anxiety. 2019. PMID: 31600020 Free PMC article.
-
The Leiden Family Lab study on Social Anxiety Disorder: A multiplex, multigenerational family study on neurocognitive endophenotypes.Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2018 Jun;27(2):e1616. doi: 10.1002/mpr.1616. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2018. PMID: 29700902 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Neurobiological Processing of Unintentional Social Norm Violations: A Multiplex, Multigenerational Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study on Social Anxiety Endophenotypes.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2020 Oct;5(10):981-990. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2020. PMID: 31031203
-
Neurobiological candidate endophenotypes of social anxiety disorder.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Dec;71:362-378. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.08.040. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016. PMID: 27593443 Review.
-
Imaging the socially-anxious brain: recent advances and future prospects.F1000Res. 2020 Apr 2;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-230. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.21214.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32269760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional seizures are associated with cerebrovascular disease and functional stroke is more common in patients with functional seizures than epileptic seizures.Epilepsy Behav. 2022 Mar;128:108582. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2022.108582. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Epilepsy Behav. 2022. PMID: 35123242 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific effects of psychedelic drug exposure on central amygdala reactivity and behavioral responding.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Apr 8;13(1):119. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02414-5. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37031219 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition and generalization of emotional and neural responses to faces associated with negative and positive feedback behaviours.Front Neurosci. 2024 Aug 5;18:1399948. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1399948. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39165343 Free PMC article.
-
ENIGMA-anxiety working group: Rationale for and organization of large-scale neuroimaging studies of anxiety disorders.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Jan;43(1):83-112. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25100. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 32618421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RDoC and Psychopathology among Youth: Misplaced Assumptions and an Agenda for Future Research.J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2020 May-Jun;49(3):322-340. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2020.1750022. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32525746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Åhs F., Gingnell M., Furmark T., Fredrikson M. Within-session effect of repeated stress exposure on extinction circuitry function in social anxiety disorder. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging. 2017;261:85–90. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Fifth Edition. 2013. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. (DSM-5)
-
- Amir N., Klumpp H., Elias J., Bedwell J.S., Yanasak N., Miller L.S. Increased activation of the anterior cingulate cortex during processing of disgust faces in individuals with social phobia. Biol. Psychiatry. 2005;57:975–981. - PubMed
-
- Amunts K., Kedo O., Kindler M., Pieperhoff P., Mohlberg H., Shah N.J., Habel U., Schneider F., Zilles K. Cytoarchitectonic mapping of the human amygdala, hippocampal region and entorhinal cortex: intersubject variability and probability maps. Anat. Embryol. (Berl). 2005;210:343–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

