Production of a specific monoclonal antibody for 1-naphthol based on novel hapten strategy and development of an easy-to-use ELISA in urine samples
- PMID: 32247241
- PMCID: PMC7200204
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110533
Production of a specific monoclonal antibody for 1-naphthol based on novel hapten strategy and development of an easy-to-use ELISA in urine samples
Abstract
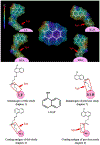
1-naphthol (1-NAP) is the main metabolite of pesticide carbaryl and naphthalene, and is also a genotoxic and carcinogenic intermediate in the synthesis of organic compound, dyes, pigment and pharmaceutical industry. In this work, two novel haptens were designed and synthesized for developing a competitive indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ciELISA) method for 1-NAP in urine samples. The assay showed a limit of detection of 2.21 ng/mL and working range from 4.02 ng/mL to 31.25 ng/mL for 1-NAP in optimized working buffer. The matrix effect of samples was eliminated via 15-fold dilution of optimized working buffer. Good average recoveries (102.4%-123.4%) with a coefficient of variation from 11.7% to 14.7% was obtained for spiked urine samples. Subsequent instrument verification test showed good correlation between the results of ciELISA and high-performance liquid chromatography. The developed ciELISA is a high-throughput tool to monitor 1-NAP in urine, which can provide technical support for the establishment of biological exposure level for the exposure to carbaryl, naphthalene and other related pollutants.
Keywords: 1-naphthol; Hapten design; Immunoassay; Monoclonal antibody.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hapten synthesis, monoclonal antibody production and immunoassay development for analyzing spiropidion residues.Food Chem. 2024 Sep 30;453:139697. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.139697. Epub 2024 May 17. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38788652
-
Immunoassay of red dyes based on the monoclonal antibody of β-naphthol.J Environ Sci Health B. 2015;50(9):645-53. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2015.1038957. J Environ Sci Health B. 2015. PMID: 26079338
-
Preparation and identification of generic antigens and broad-spectrum monoclonal antibodies for detection of organophosphorus pesticides.J AOAC Int. 2011 Nov-Dec;94(6):1911-7. doi: 10.5740/jaoacint.10-203. J AOAC Int. 2011. PMID: 22320100
-
Rational hapten design, monoclonal antibody preparation, and immunoassays development for rapid detection of fomesafen in agricultural products and soil.Food Chem. 2025 Aug 15;483:144305. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.144305. Epub 2025 Apr 13. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40250290
-
Methods for small molecule artificial hapten synthesis: A review from an organic chemist's perspective.Food Chem. 2025 Aug 1;482:143991. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143991. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40215843 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Full-length IgG Recombinant Antibody Highly Specific to Clothianidin and Its Application in Immunochromatographic Assay.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Apr 11;12(4):233. doi: 10.3390/bios12040233. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448293 Free PMC article.
-
The Simultaneous Determination of Chlorpyrifos-Ethyl and -Methyl with a New Format of Fluorescence-Based Immunochromatographic Assay.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 11;12(11):1006. doi: 10.3390/bios12111006. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421124 Free PMC article.
-
Amide-containing neoepitopes: the key factor in the preparation of hapten-specific antibodies and a strategy to overcome.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 5;14:1144020. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1144020. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37342337 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative fluorescent detection of tetracycline in animal-derived foods using quantum dots.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec 14;108(1):535. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13253-9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39673609 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a sensitive non-competitive immunoassay via immunocomplex binding peptide for the determination of ethyl carbamate in wine samples.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Mar 15;406:124288. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124288. Epub 2020 Oct 15. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 33525128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barr DB, 2008. Biomonitoring of exposure to pesticides. Journal of Chemical Health and Safety 15, 20–29.
-
- Berman T, Goeen T, Novack L, Beacher L, Grinshpan L, Segev D, Tordjman K, 2016. Urinary concentrations of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides in residents of a vegetarian community. Environ. Int. 96, 34–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

