PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in the tumor microenvironment including peritumoral tissue in primary central nervous system lymphoma
- PMID: 32248797
- PMCID: PMC7132991
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-06755-y
PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in the tumor microenvironment including peritumoral tissue in primary central nervous system lymphoma
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and PD-L2 expression on tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating immune cells in primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) remains unclear. In the present study, we analyzed needle biopsy and craniotomy specimens of patients with PCNSL to compare the PD-L1 and PD-L2 levels in the tumor and surrounding (peritumoral) tissue. We also assessed the correlation between biological factors and the prognostic significance of PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the cases of 70 patients histologically diagnosed with PCNSL (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). Immunohistochemistry for CD20, CD68, PD-L1, and PD-L2 was performed. In cases with specimens taken by craniotomy, the percentages of PD-L1- and PD-L2-positive macrophages were evaluated in both tumor and peritumoral tissue. The Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank test and Cox proportional hazard model were used for survival analysis.
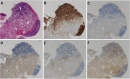
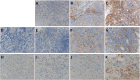
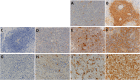
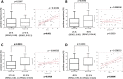
Results: The tumor cells expressed little or no PD-L1 and PD-L2, but macrophages expressed PD-L1 and PD-L2 in most of the patients. The median percentage of PD-L2-positive cells was significantly higher among peritumoral macrophages (32.5%; 95% CI: 0-94.6) than intratumoral macrophages (27.5%; 95% CI: 0-81.1, p = 0.0014). There was a significant correlation between the percentages of PD-L2-positive intratumoral macrophages and PD-L2-positive peritumoral macrophages (p = 0.0429), with very low coefficient correlation (ρ = 0.098535). PD-L1 expression on macrophages was significantly associated with biological factors (intratumoral macrophages: better KPS, p = 0.0008; better MSKCC score, p = 0.0103; peritumoral macrophages: low proportion of LDH elevation, p = 0.0064) and longer OS (for intratumoral macrophages: high PD-L1 = 60 months, 95% CI = 30-132.6; low PD-L1 = 24 months, 95% CI = 11-48; p = 0.032; for peritumoral macrophages: high PD-L1 = 60 months, 95% CI = 30.7-NR; low PD-L1 = 14 months, 95% CI = 3-26). PD-L1 expression on peritumoral macrophages was strongly predictive of a favorable outcome (HR = 0.30, 95% CI = 0.12-0.77, p = 0.0129).
Conclusions: Macrophages in intratumoral and peritumoral tissue expressed PD-L1 and PD-L2 at a higher rate than tumor cells. PD-L1 expression, especially on peritumoral macrophages, seems to be an important prognostic factor in PCNSL. Future comprehensive analysis of checkpoint molecules in the tumor microenvironment, including the peritumoral tissue, is warranted.
Keywords: Macrophage; PD-L1; PD-L2; Primary central nervous system lymphoma; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-15 expression on peritumoral macrophages is a favorable prognostic factor for primary central nervous system lymphoma patients.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):1206. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79742-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441719 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 and PD-L2 Are Differentially Expressed by Macrophages or Tumor Cells in Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, Leg Type.Am J Surg Pathol. 2018 Mar;42(3):326-334. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000983. Am J Surg Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29112015
-
Characterisation of tumour microenvironment and immune checkpoints in primary central nervous system diffuse large B cell lymphomas.Virchows Arch. 2020 Jun;476(6):891-902. doi: 10.1007/s00428-019-02695-6. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Virchows Arch. 2020. PMID: 31811434
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of PD-1/PD-L1 expression in the tumor microenvironment and neoplastic cells for lymphoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Dec;77:105999. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105999. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31704289 Review.
-
The prognostic role of PD-L1 expression for survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Oral Oncol. 2018 Nov;86:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.09.016. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Oral Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30409325
Cited by
-
Central Nervous System Lymphoma: Novel Therapies.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022 Jan;23(1):117-136. doi: 10.1007/s11864-021-00921-5. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35182298 Review.
-
PD-1 and LAG-3 Checkpoint Blockade: Potential Avenues for Therapy in B-Cell Lymphoma.Cells. 2021 May 10;10(5):1152. doi: 10.3390/cells10051152. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34068762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-scale spatial modeling of immune cell distributions enables survival prediction in primary central nervous system lymphoma.iScience. 2023 Jul 10;26(8):107331. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107331. eCollection 2023 Aug 18. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37539043 Free PMC article.
-
Primary central nervous system lymphoma.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023 Jun 15;9(1):29. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00439-0. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023. PMID: 37322012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Newcastle disease viruses expressing immunological checkpoint inhibitors induce a pro-inflammatory state and enhance tumor-specific immune responses in two murine models of cancer.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 24;15:1325558. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1325558. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38328418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Furuse M, Nonoguchi N, Omura N, Shirahata M, Iwasaki K, Inui T, Kuroiwa T, Kuwabara H, Miyatake SI. Immunotherapy of Nivolumab with dendritic cell vaccination is effective against intractable recurrent primary central nervous system lymphoma: a case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2017;57(4):191–197. doi: 10.2176/nmc.cr.2016-0330. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hayano A, Komohara Y, Takashima Y, Takeya H, Homma J, Fukai J, Iwadate Y, Kajiwara K, Ishizawa S, Hondoh H, et al. Programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in primary central nervous system lymphomas: a Clinicopathological study. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(10):5655–5666. - PubMed
-
- Cho H, Kim SH, Kim SJ, Chang JH, Yang WI, Suh CO, Kim YR, Jang JE, Cheong JW, Min YH, et al. Programmed cell death 1 expression is associated with inferior survival in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(50):87317–87328. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20264. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

