The EMPOWER-SUSTAIN e-Health Intervention to improve patient activation and self-management behaviours among individuals with Metabolic Syndrome in primary care: study protocol for a pilot randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 32248825
- PMCID: PMC7130454
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-020-04237-x
The EMPOWER-SUSTAIN e-Health Intervention to improve patient activation and self-management behaviours among individuals with Metabolic Syndrome in primary care: study protocol for a pilot randomised controlled trial
Abstract
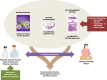
Background: Epidemiological studies conducted in various parts of the world have clearly demonstrated that metabolic syndrome (MetS) is an increasing global health problem, not only in Western societies but also in Asian populations. Web-based and mobile phone-based self-management applications have been proven to be effective in improving self-management behaviour of patients with MetS components (i.e., diabetes or hypertension). However, evidence is lacking in terms of their effectiveness specifically for patients with MetS. The aim of this pilot study is to evaluate the feasibility and potential effectiveness of the EMPOWER-SUSTAIN Self-Management e-Health Intervention in improving activation and self-management behaviours among patients with MetS. This paper presents the study protocol.
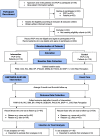
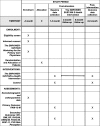
Methods: A pilot randomised controlled trial will be conducted in a university primary care clinic. A total of 232 patients aged 18-60 years with MetS will be recruited; 116 will be randomised to receive the EMPOWER-SUSTAIN intervention for 6 months, and another 116 patients will continue with usual care. The EMPOWER-SUSTAIN intervention is a multifaceted chronic disease management strategy based on the Chronic Care Model and persuasive technology theory. It consists of training primary care physicians, nurses and patients to use the EMPOWER-SUSTAIN web-based self-management mobile app, strengthening the patient-physician relationship and reinforcing the use of relevant clinical practice guidelines to guide management and prescribing. The primary outcome is the mean change in patient activation score using the Patient Activation Measure short form Malay version (PAM-13-M) questionnaire. The secondary outcomes include the changes in waist circumference, body mass index, blood pressure, patient physical activity level, eating behaviour, perception of chronic illness care, satisfaction with patient-physician interaction, and perceived absolute 10-year cardiovascular disease risk. Feasibility of implementing the intervention will be evaluated. This includes acceptability of the intervention, estimating the likely rate of participant recruitment and retention, appropriateness of the outcome measures, calculation of sample size, and the intervention's potential effectiveness.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first study in Malaysia that aims to determine the feasibility of a multifaceted e-health intervention, as well as to indicate more useful aspects of this intervention for further exploration in a larger trial.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04120779. Registered on 9 October 2019, protocol version 1.
Keywords: Chronic Care Model; Chronic disease management; E-health intervention; Metabolic syndrome; Multifaceted intervention; Patient activation; Primary care; Self-management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Study protocol of EMPOWER participatory action research (EMPOWER-PAR): a pragmatic cluster randomised controlled trial of multifaceted chronic disease management strategies to improve diabetes and hypertension outcomes in primary care.BMC Fam Pract. 2014 Sep 13;15:151. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-15-151. BMC Fam Pract. 2014. PMID: 25218689 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of the EMPOWER-PAR Intervention in Improving Clinical Outcomes of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Primary Care: A Pragmatic Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial.BMC Fam Pract. 2016 Nov 14;17(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12875-016-0557-1. BMC Fam Pract. 2016. PMID: 27842495 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Enhancing Patient Activation and Self-Management Activities in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Using the US Department of Defense Mobile Health Care Environment: Feasibility Study.J Med Internet Res. 2020 May 26;22(5):e17968. doi: 10.2196/17968. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32329438 Free PMC article.
-
Research Trends on Metabolic Syndrome in Digital Health Care Using Topic Modeling: Systematic Search of Abstracts.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Dec 12;26:e53873. doi: 10.2196/53873. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39666378 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for metabolic syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis.Acupunct Med. 2021 Aug;39(4):253-263. doi: 10.1177/0964528420960485. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Acupunct Med. 2021. PMID: 33032446
Cited by
-
Validity and reliability of the Patient Activation Measure® (PAM®)-13 Malay version among patients with Metabolic Syndrome in primary care.Malays Fam Physician. 2020 Nov 10;15(3):22-34. eCollection 2020. Malays Fam Physician. 2020. PMID: 33329860 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with usability of the EMPOWER-SUSTAIN Global Cardiovascular Risks Self-Management Booklet© among individuals with metabolic syndrome in primary care: a cross-sectional study.BMC Prim Care. 2024 Feb 3;25(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12875-024-02281-z. BMC Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 38310212 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated with High Patient Activation Level among Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome at a Primary Care Teaching Clinic.J Prim Care Community Health. 2020 Jan-Dec;11:2150132720931301. doi: 10.1177/2150132720931301. J Prim Care Community Health. 2020. PMID: 32507012 Free PMC article.
-
A Technology-Mediated Interventional Approach to the Prevention of Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jan 10;18(2):512. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18020512. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33435158 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with usability of the EMPOWER-SUSTAIN Self-management mobile app© among individuals with cardiovascular risk factors in primary care.Digit Health. 2024 Apr 3;10:20552076241242795. doi: 10.1177/20552076241242795. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38571876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–1645. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

