Effectiveness of TOcilizumab in comparison to Prednisone In Rheumatoid Arthritis patients with insufficient response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (TOPIRA): study protocol for a pragmatic trial
- PMID: 32248829
- PMCID: PMC7133012
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-020-04260-y
Effectiveness of TOcilizumab in comparison to Prednisone In Rheumatoid Arthritis patients with insufficient response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (TOPIRA): study protocol for a pragmatic trial
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease, predominantly affecting joints, which is initially treated with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs). In RA patients with insufficient response to csDMARDs, the addition of prednisone or tocilizumab, a biological DMARD (bDMARD), to the medication has been shown to be effective in reducing RA symptoms. However, which of these two treatment strategies has superior effectiveness and safety is unknown.
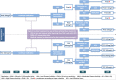
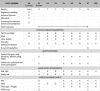
Methods: In this multicenter, investigator-initiated, open-label, randomized, pragmatic trial, we aim to recruit 120 RA patients meeting the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA, with active disease defined as a Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) > 10 and at least one swollen joint of the 28 assessed. Patients must be on stable treatment with csDMARDs for ≥ 8 weeks prior to screening and must have been treated with ≥ 2 DMARDs, of which a maximum of one tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (a class of bDMARDs) is allowed. Previous use of other bDMARDs or targeted synthetic DMARDs is not allowed. Patients will be randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either tocilizumab (subcutaneously at 162 mg/week) or prednisone (orally at 10 mg/day) as an addition to their current csDMARD therapy. Study visits will be performed at screening; baseline; and months 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 12. Study medication will be tapered in case of clinical remission (CDAI ≤ 2.8 and ≤ 1 swollen joint at two consecutive 3-monthly visits) with careful monitoring of disease activity. In case of persistent high disease activity at or after month 3 (CDAI > 22 at any visit or > 10 at two consecutive visits), patients will switch to the other strategy arm. Primary outcome is a change in CDAI from baseline to 12 months. Secondary outcomes are additional clinical response and quality of life measures, drug retention rate, radiographically detectable progression of joint damage, functional ability, and cost utility. Safety outcomes include tocilizumab-associated adverse events (AEs), glucocorticoid-associated AEs, and serious AEs.
Discussion: This will be the first randomized clinical trial comparing addition of oral prednisone or of tocilizumab head to head in RA patients with insufficient response to csDMARD therapy. It will yield important information for clinical rheumatology practice.
Trial registration: This trial was prospectively registered in the Netherlands Trial Register on October 7, 2019 (NL8070). The Netherlands Trial Register contains all items from the World Health Organization Trial Registration Data Set.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis, Tocilizumab, Prednisone, Randomized controlled trial, Insufficient response to csDMARDs.
Conflict of interest statement
JMvL has received honoraria from Arx Tx, Boehringer, Eli Lilly, Gesyntha, Leadiant, Roche, and Sanofi Genzyme and research grants from Astra Zeneca, Boehringer, MSD, Roche, and Thermofisher. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Head-to-head comparison of aggressive conventional therapy and three biological treatments and comparison of two de-escalation strategies in patients who respond to treatment: study protocol for a multicenter, randomized, open-label, blinded-assessor, phase 4 study.Trials. 2017 Apr 4;18(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-1891-x. Trials. 2017. PMID: 28376912 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term safety and effectiveness of tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate responses to csDMARDs and/or TNF inhibitors: an open-label study close to clinical practice.Clin Rheumatol. 2019 Sep;38(9):2411-2421. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04535-z. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Clin Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31028551
-
Early rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab, methotrexate, or their combination (U-Act-Early): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, strategy trial.Lancet. 2016 Jul 23;388(10042):343-355. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30363-4. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 27287832 Clinical Trial.
-
Treating to target in established rheumatoid arthritis: Challenges and opportunities in an era of novel targeted therapies and biosimilars.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2015 Aug-Dec;29(4-5):543-9. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2015.10.001. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26697765 Review.
-
EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update.Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jun;76(6):960-977. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 28264816 Review.
Cited by
-
[Safety aspects of the treatment with glucocorticoids for rheumatoid arthritis].Z Rheumatol. 2021 May;80(4):295-304. doi: 10.1007/s00393-021-00972-x. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Z Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33704557 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Baseline Glucocorticoid-Related Toxicity Scores in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Post Hoc Analysis of the GiACTA Trial.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023 Jan;5(1):51-58. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11520. Epub 2023 Jan 5. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36604825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):960–977. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Everdingen AA, Jacobs JWG, Siewertsz Van Reesema DR, Bijlsma JWJ. Low-dose prednisone therapy for patients with early active rheumatoid arthritis: clinical efficacy, disease-modifying properties, and side effects: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Ann Intern Med. 2002;136(1):1–12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-1-200201010-00006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bakker MF, Jacobs JWG, Welsing PMJ, Verstappen SMM, Tekstra J, Ton E, et al. Low-dose prednisone inclusion in a methotrexate-based, tight control strategy for early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(5):329–339. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-156-5-201203060-00004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

