Impact of comorbidity on health-related quality of life among type 2 diabetic patients in primary care
- PMID: 32248877
- PMCID: PMC7137353
- DOI: 10.1017/S1463423620000055
Impact of comorbidity on health-related quality of life among type 2 diabetic patients in primary care
Abstract
Background: Health-related quality of life (HRQL) is an important outcome for chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus that is associated with complications, comorbidities, and lifelong care.
Objectives: The present study aims to explore the impact of comorbidities on the different dimensions of HRQL among type 2 diabetic patients attending primary care.
Methods: A total of 912 type 2 diabetic patients attending primary care centers in India were assessed using a predesigned and pretested questionnaire - Diabetes Comorbidity Evaluation Tool in Primary Care. The HRQL was measured by physical and mental health summary scores [physical component summary (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS)] of the Short Form Health Survey 12. The associations of sociodemographic variables and clinical variables with PCS and MCS were assessed, and a minimal difference of 5 in the scores (on a scale of 0-100) was kept as clinically relevant difference for this study. Mean differences in mental (MCS) and physical (PCS) scores of quality of life by number and type of comorbid conditions in type 2 diabetic patients were calculated.
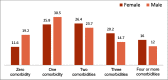
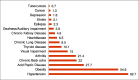
Result: The presence of comorbid conditions was associated with lower scores of PCS and MCS (P < 0.001). Significant reduction in HRQL was found with increase in number of comorbid conditions, and negative association was established between the number of comorbidities and the PCS (r = -0.25, P < 0.0001) and MCS scores (r = -0.21, P < 0.0001). Among comorbidities, acid peptic disease, chronic lung disease, visual impairment, depression, and stroke had significantly and clinically relevant reduced scores. Duration of diabetes, use of insulin, and obesity were also associated with poor HRQL.
Conclusion: Comorbidities considerably impair the HRQL among type 2 diabetic patients. National programs designed for diabetes management should also take into account the challenges of coexisting chronic conditions and its substantial effect on HRQL.
Keywords: SF-12; comorbidity; health-related quality of life; primary care; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health-related quality of life (HRQL) for individuals with self-reported chronic physical and/or mental health conditions: panel survey of an adult sample in the United States.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2012 Dec 19;10:154. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-10-154. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2012. PMID: 23253258 Free PMC article.
-
Can metabolic control variables of diabetic patients predict their quality of life?J Am Soc Hypertens. 2016 Jan;10(1):81-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2015.11.014. Epub 2015 Nov 26. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26850525
-
Incremental effects of comorbidity on quality of life in patients with psoriatic arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2013 Aug;40(8):1349-56. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.121500. Epub 2013 Jun 15. J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23772076
-
Quality of life of Latin-American individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review.Prim Care Diabetes. 2020 Aug;14(4):317-334. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2019.09.003. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Prim Care Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 31564515
-
Diabetes-Associated Comorbidities.Prim Care. 2022 Jun;49(2):275-286. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2021.11.004. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Prim Care. 2022. PMID: 35595482 Review.
Cited by
-
Musculoskeletal Comorbidities among known Diabetes Patients, their Quality of Life, and Healthcare Costs: A Comparative Study From a Tertiary Care Hospital in Uttarakhand.Indian J Community Med. 2024 Jan-Feb;49(1):76-81. doi: 10.4103/ijcm.ijcm_832_22. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Indian J Community Med. 2024. PMID: 38425961 Free PMC article.
-
The socio-demographic and lifestyle characteristics associated with quality of life among diabetic patients in Lebanon: a cross-sectional study.Pharm Pract (Granada). 2023 Jan-Mar;21(1):2775. doi: 10.18549/PharmPract.2023.1.2775. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2023. PMID: 37090463 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Underlying Conditions on Quality-of-Life Measurement Among Patients with Chronic Wounds, as Measured by Utility Values: A Review with an Additional Study.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2023 Dec;12(12):680-695. doi: 10.1089/wound.2023.0098. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2023. PMID: 37815559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of medical comorbidity, cognition, and age on patient-reported outcomes in Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2023 Nov;116:105892. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2023.105892. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 37837675 Free PMC article.
-
A Problem in NIH and Federally Funded Prostate Cancer Interventional Clinical Trials.J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2024 Oct;11(5):2740-2755. doi: 10.1007/s40615-023-01737-9. Epub 2023 Aug 8. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2024. PMID: 37552424
References
-
- Agborsangaya CB, Lau D, Lahtinen M, Cooke T and Johnson JA (2013) Health-related quality of life and healthcare utilization in multimorbidity: results of a cross-sectional survey. Quality of Life Research 22, 791–799. - PubMed
-
- Alonso J, Ferrer M, Gandek B, Ware JE, Aaronson NK, Mosconi P, Rasmussen NK, Bullinger M, Fukuhara S, Kaasa S and Leplège A (2004) Health-related quality of life associated with chronic conditions in eight countries: results from the International Quality of Life Assessment (IQOLA) Project. Quality of Life Research 13, 283–298. - PubMed
-
- Anon (2015) Census 2011 India Retrieved 30 March 2019 from https://www.census2011.co.in/census/city/270-bhubaneswar.html
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical