Structure-Activity Relationship of Phenylpyrazolones against Trypanosoma cruzi
- PMID: 32249532
- PMCID: PMC7496920
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202000136
Structure-Activity Relationship of Phenylpyrazolones against Trypanosoma cruzi
Abstract
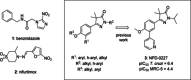
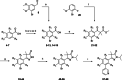
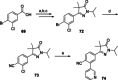
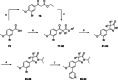
Chagas disease is a neglected parasitic disease caused by the parasitic protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi and currently affects around 8 million people. Previously, 2-isopropyl-5-(4-methoxy-3-(pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one (NPD-0227) was discovered to be a sub-micromolar inhibitor (pIC50 =6.4) of T. cruzi. So far, SAR investigations of this scaffold have focused on the alkoxy substituent, the pyrazolone nitrogen substituent and the aromatic substituent of the core phenylpyrazolone. In this study, modifications of the phenyldihydropyrazolone scaffold are described. Variations were introduced by installing different substituents on the phenyl core, modifying the geminal dimethyl and installing various bio-isosteres of the dihydropyrazolone group. The anti T. cruzi activity of NPD-0227 could not be surpassed as the most potent compounds show pIC50 values of around 6.3. However, valuable additional SAR data for this interesting scaffold was obtained, and the data suggest that a scaffold hop is feasible as the pyrazolone moiety can be replaced by a oxazole or oxadiazole with minimal loss of activity.
Keywords: Benznidazole; Trypanosoma cruzi; neglected parasitic diseases; phenylpyrazolones; structure-activity relationships.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
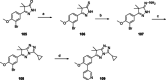
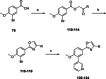
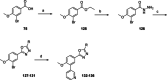
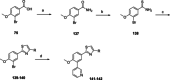
References
-
- None
-
- Rassi A., Rassi A., Marcondes de Rezende J., Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 275–291. - PubMed
-
- None
-
- WHO, Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis), Vol. 2018, WHO, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs340/en/, 2018;
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

