Repeated courses of low-dose 2 × 2 Gy radiation therapy in patients with indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas
- PMID: 32249547
- PMCID: PMC7286454
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2796
Repeated courses of low-dose 2 × 2 Gy radiation therapy in patients with indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas
Abstract
Purpose: In patients with indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (B-NHL), one course of low-dose radiotherapy (LD-RT) 2 × 2 Gy is emerging as new option of therapy in palliative setting. Efficacy of LD-RT when repeated remains to be determinate. This study aims to assess the efficacy of repeated LD-RT given in patients with indolent B-NHL.
Materials and methods: All consecutive adult patients who received two or more courses of LD-RT 2 × 2 Gy for indolent B-NHL at Gustave Roussy institution, during the period 1990-2015 were retrospectively investigated.
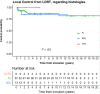
Results: Thirty-three patients received two or more courses of LD-RT for indolent B-NHL during the study period. The median age was 57 (range 37-80) years, histological types were distributed among follicular lymphoma (n = 24 pts; 73%), marginal-zone lymphoma (n = 6 pts; 18%), and primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma (n = 3 pts; 9%). The median number of low-dose radiation therapy courses given per patients was 2 (range 2-6). The overall response rates following the first and the second course of LD-RT were 96% and 88%, respectively (P = .31). The 1- and 2-years local control rates following the first courses of LD-RT were 94% (CI 95: 86-100) and 94% (CI 95: 86-98); and were 91% (CI 95: 82-100) and 88% (CI 95: 77-100) following the second course of LD-RT (P = .39).
Conclusion: The repeated courses of LD-RT offered similar efficacy compare with the first course in patients with indolent B-NHL. LD-RT repeated is a simple, easy to give, and non-toxic asset that could be investigated as treatment option in patients with indolent B-NHL.
Keywords: follicular lymphoma; indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; low-dose radiotherapy; marginal zone lymphoma; primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Jean‐Marie Michot: Principal/sub‐Investigator of Clinical Trials for: Abbvie, Aduro, Agios, Amgen, Argen‐x, Astex, AstraZeneca, Aveo pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Beigene, Blueprint, BMS, Boeringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Chugai, Clovis, Daiichi Sankyo, Debiopharm, Eisai, Eos, Exelixis, Forma, Gamamabs, Genentech, Gortec, GSK, H3 biomedecine, Incyte, Innate Pharma, Janssen, Kura Oncology, Kyowa, Lilly, Loxo, Lysarc, Lytix Biopharma, Medimmune, Menarini, Merus, MSD, Nanobiotix, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis, Octimet, Oncoethix, Oncopeptides AB, Orion, Pfizer, Pharmamar, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Sanofi, Servier, Sierra Oncology, Taiho, Takeda, Tesaro, Xencor. PERSONAL FEES (Monies paid to you for services rendered, generally honoraria, royalties or fees for consulting, lectures, speakers bureaus, expert testimony, employment, ad‐boards, etc): Roche, Celgene, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Janssen. Vincent Ribrag: Principal/sub‐Investigator of Clinical Trials for: Abbvie, Aduro, Agios, Amgen, Argen‐x, Astex, AstraZeneca, Aveo pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Beigene, Blueprint, BMS, Boeringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Chugai, Clovis, Daiichi Sankyo, Debiopharm, Eisai, Eos, Exelixis, Forma, Gamamabs, Genentech, Gortec, GSK, H3 biomedecine, Incyte, Innate Pharma, Janssen, Kura Oncology, Kyowa, Lilly, Loxo, Lysarc, Lytix Biopharma, Medimmune, Menarini, Merus, MSD, Nanobiotix, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis, Octimet, Oncoethix, Oncopeptides AB, Orion, Pfizer, Pharmamar, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Sanofi, Servier, Sierra Oncology, Taiho, Takeda, Tesaro, Xencor. PERSONAL FEES (Monies paid to you for services rendered, generally honoraria, royalties or fees for consulting, lectures, speakers bureaus, expert testimony, employment, ad‐boards, etc): Medimmune, Pfizer, Servier, AstraZeneca, Janssen Bristol‐Myers Squibb. Other authors: nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Haas R, Poortmans PH, de Jong D, et al. High response rates and lasting remissions after low‐dose involved field radiotherapy in indolent lymphomas. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(13):2474‐2480. - PubMed
-
- Specht L. Radiotherapy for indolent lymphomas: how much is enough? Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:372‐374. - PubMed
-
- Campbell BA, Voss N, Woods R, et al. Long‐term outcomes for patients with limited stage follicular lymphoma: involved regional radiotherapy versus involved node radiotherapy. Cancer. 2010;116:3797‐3806. - PubMed
-
- Pugh TJ, Ballonoff A, Newman F, Rabinovitch R. Improved survival in patients with early stage low‐grade follicular lymphoma treated with radiation: a Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database analysis. Cancer. 2010;116:3843‐3851. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

