Potential harmful effects of discontinuing ACE-inhibitors and ARBs in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 32250244
- PMCID: PMC7198232
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.57278
Potential harmful effects of discontinuing ACE-inhibitors and ARBs in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
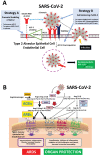
The discovery of angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) as the receptor for SARS- CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2) has implicated the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and respiratory failure in patients with coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19). The angiotensin converting enzyme-1-angiotensin II-angiotensin AT1 receptor pathway contributes to the pathophysiology of ARDS, whereas activation of the ACE-2-angiotensin(1-7)-angiotensin AT2 receptor and the ACE-2-angiotensin(1-7)-Mas receptor pathways have been shown to be protective. Here we propose and discuss therapeutic considerations how to increase soluble ACE-2 in plasma in order for ACE-2 to capture and thereby inactivate SARS-CoV-2. This could be achieved by administering recombinant soluble ACE-2. We also discuss why and how ACEIs and ARBs provide cardiovascular, renal and also pulmonary protection in SARS-CoV-2- associated ARDS. Discontinuing these medications in COVID-19 patients may therefore potentially be harmful.
Keywords: ACE; ACE inhibitor; ACE inhibitors; ACE-2; ACEIs; ARBs; ARDS; Acute respiratory distress syndrome; COVID-19; RAAS; SARS; SARS-CoV-2; angiotensin; angiotensin receptor antagonists; angiotensin receptor blocker; angiotensin-converting enzyme-1; angiotensin-converting enzyme-2; arterial hypertension; cardiovascular; coronavirus; human biology; infection; medicine; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; therapy; treatment; virus.
© 2020, Rossi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
GR, VS No competing interests declared, MB Senior Editor, eLife
Figures
References
-
- Bozkurt B, Kovacs R, Harrington B. HFSA/ACC/AHA Statement Addresses Concerns Re: Using RAAS Antagonists in COVID-19. American College of Cardiology; 2020. https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/articles/2020/03/17/08/59/hfsa-... - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

