The effects of aripiprazole and olanzapine on pupillary light reflex and its relationship with pharmacogenetics in a randomized multiple-dose trial
- PMID: 32250470
- PMCID: PMC7495280
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.14300
The effects of aripiprazole and olanzapine on pupillary light reflex and its relationship with pharmacogenetics in a randomized multiple-dose trial
Abstract
Aims: Pupillography is a noninvasive and cost-effective method to determine autonomic nerve activity. Genetic variants in cytochrome P450 (CYP), dopamine receptor (DRD2, DRD3), serotonin receptor (HTR2A, HTR2C) and ATP-binding cassette subfamily B (ABCB1) genes, among others, were previously associated with the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antipsychotic drugs. Our aim was to evaluate the effects of aripiprazole and olanzapine on pupillary light reflex related to pharmacogenetics.
Methods: Twenty-four healthy volunteers receiving 5 oral doses of 10 mg aripiprazole and 5 mg olanzapine tablets were genotyped for 46 polymorphisms by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Pupil examination was performed by automated pupillometry. Aripiprazole, dehydro-aripiprazole and olanzapine plasma concentrations were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
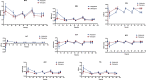
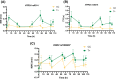
Results: Aripiprazole affected pupil contraction: it caused dilatation after the administration of the first dose, then caused constriction after each dosing. It induced changes in all pupillometric parameters (P < .05). Olanzapine only altered minimum pupil size (P = .046). Polymorphisms in CYP3A, HTR2A, UGT1A1, DRD2 and ABCB1 affected pupil size, the time of onset of constriction, pupil recovery and constriction velocity. Aripiprazole, dehydro-aripiprazole and olanzapine pharmacokinetics were significantly affected by polymorphisms in CYP2D6, CYP3A, CYP1A2, ABCB1 and UGT1A1 genes.
Conclusions: In conclusion, aripiprazole and its main metabolite, dehydro-aripiprazole altered pupil contraction, but olanzapine did not have such an effect. Many polymorphisms may influence pupillometric parameters and several polymorphisms had an effect on aripiprazole, dehydro-aripiprazole and olanzapine pharmacokinetics. Pupillography could be a useful tool for the determination of autonomic nerve activity during antipsychotic treatment.
Keywords: antipsychotics; genetics and pharmacogenetics; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; schizophrenia.
© 2020 The Authors. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
F. Abad‐Santos and D. Ochoa have been consultants or investigators in clinical trials sponsored by the following pharmaceutical companies: Abbott, Alter, Chemo, Cinfa, FAES, Farmalíder, Ferrer, GlaxoSmithKline, Galenicum, Gilead, Janssen‐Cilag, Kern, Normon, Novartis, Servier, Silverpharma, Teva and Zambon. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic Polymorphisms Associated With the Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Adverse Effects of Olanzapine, Aripiprazole and Risperidone.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 14;12:711940. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.711940. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34335273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of aripiprazole on pupillometric parameters related to pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics after single oral administration to healthy subjects.J Psychopharmacol. 2018 Nov;32(11):1212-1222. doi: 10.1177/0269881118798605. Epub 2018 Sep 25. J Psychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30251598 Clinical Trial.
-
Metabolic Effects of Aripiprazole and Olanzapine Multiple-Dose Treatment in a Randomised Crossover Clinical Trial in Healthy Volunteers: Association with Pharmacogenetics.Adv Ther. 2021 Feb;38(2):1035-1054. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01566-w. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 33278020 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of aripiprazole on circadian prolactin secretion related to pharmacogenetics in healthy volunteers.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020 Mar;126(3):236-246. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13323. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31520576 Clinical Trial.
-
Aripiprazole: a review of its use in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.Drugs. 2004;64(15):1715-36. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464150-00010. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15257633 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacogenetics and Schizophrenia-Can Genomics Improve the Treatment with Second-Generation Antipsychotics?Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 7;10(12):3165. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123165. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of Opioids on Pupil Initial Diameter and Pupillary Dilation Velocity in ICU Patients.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2025 Jul;69(6):e70080. doi: 10.1111/aas.70080. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2025. PMID: 40550493 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotic drug-aripiprazole against schizophrenia, its therapeutic and metabolic effects associated with gene polymorphisms.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Feb;75(1):19-31. doi: 10.1007/s43440-022-00440-6. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36526889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Polymorphisms Associated With the Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Adverse Effects of Olanzapine, Aripiprazole and Risperidone.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 14;12:711940. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.711940. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34335273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenging pharmacotherapy management of a psychotic disorder due to a delicate pharmacogenetic profile and drug-drug interactions: a case report and literature review.Croat Med J. 2024 Aug 31;65(4):383-395. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2024.65.383. Croat Med J. 2024. PMID: 39219201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Conley RR, Kelly DL. Second‐generation antipsychotics for schizophrenia: a review of clinical pharmacology and medication‐associated side effects. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci. 2005;42(1):51‐60. - PubMed
-
- Bhana N, Foster RH, Olney R, Plosker GL. Olanzapine: an updated review of its use in the management of schizophrenia. Drugs. 2001;61(1):111‐161. - PubMed
-
- McGavin JK, Goa KL. Aripiprazole. CNS Drugs. 2002;16(11):779‐786. discussion 787–788 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

