Report From the International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consultation Conference on Molecular Pathology of Urogenital Cancers: III: Molecular Pathology of Kidney Cancer
- PMID: 32251007
- PMCID: PMC7289677
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001476
Report From the International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consultation Conference on Molecular Pathology of Urogenital Cancers: III: Molecular Pathology of Kidney Cancer
Abstract
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) subtypes are increasingly being discerned via their molecular underpinnings. Frequently this can be correlated to histologic and immunohistochemical surrogates, such that only simple targeted molecular assays, or none at all, are needed for diagnostic confirmation. In clear cell RCC, VHL mutation and 3p loss are well known; however, other genes with emerging important roles include SETD2, BAP1, and PBRM1, among others. Papillary RCC type 2 is now known to include likely several different molecular entities, such as fumarate hydratase (FH) deficient RCC. In MIT family translocation RCC, an increasing number of gene fusions are now described. Some TFE3 fusion partners, such as NONO, GRIPAP1, RBMX, and RBM10 may show a deceptive fluorescence in situ hybridization result due to the proximity of the genes on the same chromosome. FH and succinate dehydrogenase deficient RCC have implications for patient counseling due to heritable syndromes and the aggressiveness of FH-deficient RCC. Immunohistochemistry is increasingly available and helpful for recognizing both. Emerging tumor types with strong evidence for distinct diagnostic entities include eosinophilic solid and cystic RCC and TFEB/VEGFA/6p21 amplified RCC. Other emerging entities that are less clearly understood include TCEB1 mutated RCC, RCC with ALK rearrangement, renal neoplasms with mutations of TSC2 or MTOR, and RCC with fibromuscular stroma. In metastatic RCC, the role of molecular studies is not entirely defined at present, although there may be an increasing role for genomic analysis related to specific therapy pathways, such as for tyrosine kinase or MTOR inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



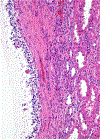


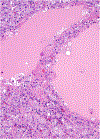
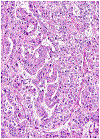
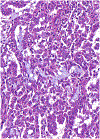
References
-
- Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, et al. The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part A: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol. 2016;70:93–105. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Jonasch E, Agarwal N, et al. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) Kidney Cancer. 2019. Available at: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/kidney.pdf. Accessed 8/28/2019.
-
- Srigley JR, Delahunt B, Eble JN, et al. The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Vancouver classification of renal neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37:1469–1489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

