Size-selective molecular recognition based on a confined DNA molecular sieve using cavity-tunable framework nucleic acids
- PMID: 32251279
- PMCID: PMC7089997
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15297-7
Size-selective molecular recognition based on a confined DNA molecular sieve using cavity-tunable framework nucleic acids
Abstract
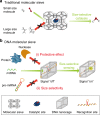
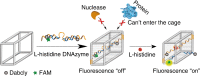
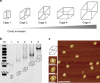
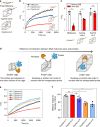
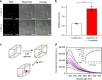
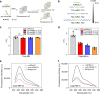
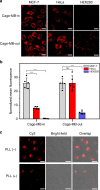
Size selectivity is an important mechanism for molecular recognition based on the size difference between targets and non-targets. However, rational design of an artificial size-selective molecular recognition system for biological targets in living cells remains challenging. Herein, we construct a DNA molecular sieve for size-selective molecular recognition to improve the biosensing selectivity in living cells. The system consists of functional nucleic acid probes (e.g., DNAzymes, aptamers and molecular beacons) encapsulated into the inner cavity of framework nucleic acid. Thus, small target molecules are able to enter the cavity for efficient molecular recognition, while large molecules are prohibited. The system not only effectively protect probes from nuclease degradation and nonspecific proteins binding, but also successfully realize size-selective discrimination between mature microRNA and precursor microRNA in living cells. Therefore, the DNA molecular sieve provides a simple, general, efficient and controllable approach for size-selective molecular recognition in biomedical studies and clinical diagnoses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Confined DNA tetrahedral molecular sieve for size-selective electrochemiluminescence sensing.Anal Chim Acta. 2024 May 22;1304:342561. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2024.342561. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Anal Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38637057
-
Functional Nucleic Acids for Pathogenic Bacteria Detection.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Sep 21;54(18):3540-3549. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00355. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34478272
-
Electrochemical sensing of L-histidine based on structure-switching DNAzymes and gold nanoparticle-graphene nanosheet composites.Chem Commun (Camb). 2011 May 21;47(19):5476-8. doi: 10.1039/c1cc10965k. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011. PMID: 21483916
-
Advances of functional nucleic acids based on specific recognition:A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Apr;304(Pt 1):140828. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140828. Epub 2025 Feb 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39929457 Review.
-
Peroxidase-mimicking DNAzymes for biosensing applications: a review.Anal Chim Acta. 2011 Nov 30;707(1-2):7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.08.050. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Anal Chim Acta. 2011. PMID: 22027115 Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamer-functionalized field-effect transistor biosensors for disease diagnosis and environmental monitoring.Exploration (Beijing). 2023 May 11;3(3):20210027. doi: 10.1002/EXP.20210027. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exploration (Beijing). 2023. PMID: 37933385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transformation of a Pd6 trifacial barrel to a Pd8 tetrafacial barrel by C70 as guest and oxidative photolysis of alkenes using the C70 encapsulated barrel under red light.Chem Sci. 2025 Jun 5;16(28):12885-12895. doi: 10.1039/d5sc01015b. eCollection 2025 Jul 16. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40521109 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Application of DNAzyme-based Nanodevices.Chem Res Chin Univ. 2023;39(1):42-60. doi: 10.1007/s40242-023-2334-8. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Chem Res Chin Univ. 2023. PMID: 36687211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamer Blocking Strategy Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Virus Infection.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Apr 26;60(18):10266-10272. doi: 10.1002/anie.202100225. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33561300 Free PMC article.
-
Spatially Localized Entropy-Driven Evolution of Nucleic Acid-Based Constitutional Dynamic Networks for Intracellular Imaging and Spatiotemporal Programmable Gene Therapy.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Jul 31;146(30):20685-20699. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c03651. Epub 2024 Jul 16. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 39012486 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

