Folic acid supplementation alleviates reduced ureteric branching, nephrogenesis, and global DNA methylation induced by maternal nutrient restriction in rat embryonic kidney
- PMID: 32251454
- PMCID: PMC7135271
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230289
Folic acid supplementation alleviates reduced ureteric branching, nephrogenesis, and global DNA methylation induced by maternal nutrient restriction in rat embryonic kidney
Abstract
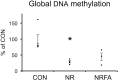
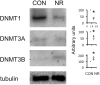
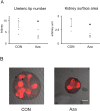
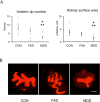
We previously reported that maternal nutrient restriction (NR) inhibited ureteric branching, metanephric growth, and nephrogenesis in the rat. Here we examined whether folic acid, a methyl-group donor, rescues the inhibition of kidney development induced by NR and whether DNA methylation is involved in it. The offspring of dams given food ad libitum (CON) and those subjected to 50% food restriction (NR) were examined. NR significantly reduced ureteric tip number at embryonic day 14, which was attenuated by folic acid supplementation to nutrient restricted dams. At embryonic day 18, glomerular number, kidney weight, and global DNA methylation were reduced by NR, and maternal folic acid supplementation again alleviated them. Among DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), DNMT1 was strongly expressed at embryonic day 15 in CON but was reduced in NR. In organ culture, an inhibitor of DNA methylation 5-aza-2 '-deoxycytidine as well as medium lacking methyl donors folic acid, choline, and methionine, significantly decreased ureteric tip number and kidney size mimicking the effect of NR. In conclusion, global DNA methylation is necessary for normal kidney development. Folic acid supplementation to nutrient restricted dams alleviated the impaired kidney development and DNA methylation in the offspring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Maternal nutrient restriction inhibits ureteric bud branching but does not affect the duration of nephrogenesis in rats.Pediatr Res. 2015 May;77(5):633-9. doi: 10.1038/pr.2015.24. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Pediatr Res. 2015. PMID: 25675424
-
Effect of maternal and postweaning folic acid supplementation on colorectal cancer risk in the offspring.Gut. 2011 Dec;60(12):1687-94. doi: 10.1136/gut.2011.238782. Epub 2011 May 11. Gut. 2011. PMID: 21561879
-
Effect of Folic Acid Supplementation on Renal Phenotype and Epigenotype in Early Weanling Intrauterine Growth Retarded Rats.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2015;40(4):395-402. doi: 10.1159/000368516. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2015. PMID: 26202812
-
Maternal nutrient restriction alters renal development and blood pressure regulation of the offspring.Proc Nutr Soc. 2006 Feb;65(1):116-24. doi: 10.1079/pns2005484. Proc Nutr Soc. 2006. PMID: 16441951 Review.
-
Effect of DNA Methylation in Various Diseases and the Probable Protective Role of Nutrition: A Mini-Review.Cureus. 2015 Aug 24;7(8):e309. doi: 10.7759/cureus.309. Cureus. 2015. PMID: 26430583 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal periconceptional folic acid supplementation and risk for fetal congenital genitourinary system defects.Pediatr Res. 2024 Mar;95(4):1132-1138. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02808-7. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 37709853
-
Effect of Ethanol-Induced Methyl Donors Consumption on the State of Hypomethylation in Cervical Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 23;24(9):7729. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097729. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175434 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional changes in the kidney caused by adverse fetal and neonatal environments.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Mar;49(3):2335-2344. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06967-w. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34817775 Review.
-
The Impact of Gestational Diabetes on Kidney Development: is There an Epigenetic Link?Curr Diab Rep. 2024 Dec 18;25(1):13. doi: 10.1007/s11892-024-01569-9. Curr Diab Rep. 2024. PMID: 39690358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphometric analysis of the intergenerational effects of protein restriction on nephron endowment in mice.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 18;10(20):e39552. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39552. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39498088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gopalakrishnan GS, Gardner DS, Dandrea J, Langley-Evans SC, Pearce S, Kurlak LO, et al. Influence of maternal pre-pregnancy body composition and diet during early-mid pregnancy on cardiovascular function and nephron number in juvenile sheep. Br J Nutr. 2005;94(6):938–47. 10.1079/bjn20051559 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

