Elevation of the Blood Glucose Level is Involved in an Increase in Expression of Sweet Taste Receptors in Taste Buds of Rat Circumvallate Papillae
- PMID: 32252371
- PMCID: PMC7230327
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12040990
Elevation of the Blood Glucose Level is Involved in an Increase in Expression of Sweet Taste Receptors in Taste Buds of Rat Circumvallate Papillae
Abstract
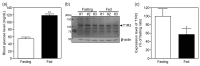
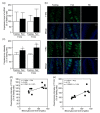
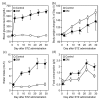
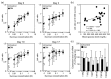
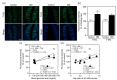
The gustation system for sweeteners is well-known to be regulated by nutritional and metabolic conditions, but there is no or little information on the underlying mechanism. Here, we examined whether elevation of the blood glucose level was involved in alteration of the expression of sweet taste receptors in circumvallate papillae (CP) and sweet taste sensitivity in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Rats under 4 h-fed conditions following 18 h-fasting exhibited elevated blood glucose levels and decreased pancreatic T1R3 expression, compared to rats after 18 h-fasting treatment, and they exhibited increased protein expression of sweet taste receptors T1R2 and T1R3 in CP. Under streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes mellites (DM) conditions, the protein expression levels of T1R2 and T1R3 in CP were higher than those under control conditions, and these DM rats exhibited increased lick ratios in a low sucrose concentration range in a brief access test with a mixture of sucrose and quinine hydrochloride (QHCl). These findings indicate that the elevation of blood glucose level is a regulator for an increase in sweet taste receptor protein expression in rat CP, and such alteration in STZ-induced DM rats is involved in enhancement of their sweet taste sensitivity.
Keywords: blood glucose level; diabetes mellites; fasting and fed condition; gustation; sweet taste; taste bud.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nakagawa Y., Nagasawa M., Mogami H., Lohse M., Ninomiya Y., Kojima I. Multimodal function of the sweet taste receptor expressed in pancreatic beta-cells: Generation of diverse patterns of intracellular signals by sweet agonists. Endocr. J. 2013;60:1191–1206. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ13-0282. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa Y., Nagasawa M., Yamada S., Hara A., Mogami H., Nikolaev V.O., Lohse M.J., Shigemura N., Ninomiya Y., Kojima I. Sweet taste receptor expressed in pancreatic beta-cells activates the calcium and cyclic AMP signaling systems and stimulates insulin secretion. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e5106. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

