Dual Angiotensin Receptor and Neprilysin Inhibitor Ameliorates Portal Hypertension in Portal Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 32252377
- PMCID: PMC7238216
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12040320
Dual Angiotensin Receptor and Neprilysin Inhibitor Ameliorates Portal Hypertension in Portal Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
Background: Portal hypertension is characterized by exaggerated activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis. Natriuretic peptide system plays a counter-regulatory role, which is modulated by neprilysin. LCZ696 (sacubitril/valsartan) is a dual angiotensin receptor and neprilysin inhibitor. This study evaluated the effect of LCZ696 on portal hypertensive rats.
Methods: Portal hypertension was induced by partial portal vein ligation (PVL) in rats. LCZ696, valsartan (angiotensin receptor blocker), or normal saline (control) was administered in PVL rats for 10 days. Then, hemodynamic and biochemistry data were obtained. The hepatic histology and protein expressions were surveyed. On the parallel groups, the portal-systemic shunting degrees were determined.
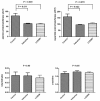
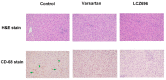
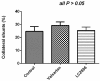
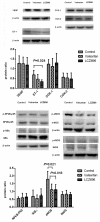
Results: LCZ696 and valsartan reduced mean arterial pressure and systemic vascular resistance. LCZ696, but not valsartan, reduced portal pressure in portal hypertensive rats (control vs. valsartan vs. LCZ696: 15.4 ± 1.6 vs. 14.0 ± 2.3 vs. 12.0 ± 2.0 mmHg, control vs. LCZ696: P < 0.05). LCZ696 and valsartan improved liver biochemistry data and reduced intrahepatic Cluster of Differentiation 68 (CD68)-stained macrophages infiltration. Hepatic endothelin-1 (ET-1) protein expression was downregulated by LCZ696. The portal-systemic shunting was not affected by LCZ696 and valsartan.
Conclusion: LCZ696 and valsartan reduced mean arterial pressure through peripheral vasodilation. Furthermore, LCZ696 significantly reduced portal pressure in PVL rats via hepatic ET-1 downregulation.
Keywords: angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor; natriuretic peptide; portal hypertension; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual angiotensin receptor and neprilysin inhibitor reduced portal pressure through peripheral vasodilatation and decreasing systemic arterial pressure in cirrhotic rats.J Chin Med Assoc. 2023 Sep 1;86(9):786-794. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000959. Epub 2023 Jul 18. J Chin Med Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37462441
-
Angiotensin II Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitor Sacubitril/Valsartan Improves Endothelial Dysfunction in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Oct 17;6(10):e006617. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006617. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 29042424 Free PMC article.
-
AHU377+Valsartan (LCZ696) Modulates Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) in the Cardiac of Female Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Compared With Valsartan.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Sep;24(5):450-459. doi: 10.1177/1074248419838503. Epub 2019 Apr 25. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31023080
-
Dual Angiotensin Receptor and Neprilysin Inhibition with Sacubitril/Valsartan in Chronic Systolic Heart Failure: Understanding the New PARADIGM.Ann Pharmacother. 2015 Nov;49(11):1237-51. doi: 10.1177/1060028015593093. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Ann Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26175499 Review.
-
Combined Angiotensin Receptor Antagonism and Neprilysin Inhibition.Circulation. 2016 Mar 15;133(11):1115-24. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018622. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 26976916 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin II receptor Neprilysin inhibitor (LCZ696) compared to Valsartan attenuates Hepatotoxicity in STZ-induced hyperglycemic rats.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Oct 22;17(18):3098-3106. doi: 10.7150/ijms.49373. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33173431 Free PMC article.
-
The Renin-Angiotensin System in Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 27;25(11):5807. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115807. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated serum neprilysin levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: hepatic oxidative stress as an underlying mechanism.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Dec 26;52(1):81. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10152-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39722039
-
Molecular mechanisms of sacubitril/valsartan in cardiac remodeling.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 8;13:892460. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.892460. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36003518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitor (ARNI) and Cardiac Arrhythmias.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 20;22(16):8994. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168994. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445698 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

