Artificial Intelligence in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
- PMID: 32252506
- PMCID: PMC7137570
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2020.038
Artificial Intelligence in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Abstract
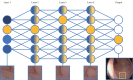
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly integrating into modern technology and clinical practice. Although in its nascency, AI has become a hot topic of investigation for applications in clinical practice. Multiple fields of medicine have embraced the possibility of a future with AI assisting in diagnosis and pathology applications. In the field of gastroenterology, AI has been studied as a tool to assist in risk stratification, diagnosis, and pathologic identification. Specifically, AI has become of great interest in endoscopy as a technology with substantial potential to revolutionize the practice of a modern gastroenterologist. From cancer screening to automated report generation, AI has touched upon all aspects of modern endoscopy. Here, we review landmark AI developments in endoscopy. Starting with broad definitions to develop understanding, we will summarize the current state of AI research and its potential applications. With innovation developing rapidly, this article touches upon the remarkable advances in AI-assisted endoscopy since its initial evaluation at the turn of the millennium, and the potential impact these AI models may have on the modern clinical practice. As with any discussion of new technology, its limitations must also be understood to apply clinical AI tools successfully.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Colonoscopy; Computer assisted diagnosis; Early detection of cancer; Endoscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Silver D, Huang A, Maddison CJ, et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature. 2016;529:484–489. - PubMed
-
- Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA. 2016;316:2402–2410. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

