Atrial Fibrillation Risk and Discrimination of Cardioembolic From Noncardioembolic Stroke
- PMID: 32252601
- PMCID: PMC7188588
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.028837
Atrial Fibrillation Risk and Discrimination of Cardioembolic From Noncardioembolic Stroke
Abstract
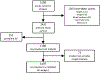
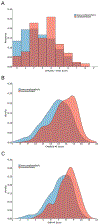
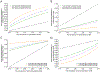
Background and Purpose- Classification of stroke as cardioembolic in etiology can be challenging, particularly since the predominant cause, atrial fibrillation (AF), may not be present at the time of stroke. Efficient tools that discriminate cardioembolic from noncardioembolic strokes may improve care as anticoagulation is frequently indicated after cardioembolism. We sought to assess and quantify the discriminative power of AF risk as a classifier for cardioembolism in a real-world population of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Methods- We performed a cross-sectional analysis of a multi-institutional sample of patients with acute ischemic stroke. We systematically adjudicated stroke subtype and examined associations between AF risk using CHA2DS2-VASc, Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology-AF score, and the recently developed Electronic Health Record-Based AF score, and cardioembolic stroke using logistic regression. We compared the ability of AF risk to discriminate cardioembolism by calculating C statistics and sensitivity/specificity cutoffs for cardioembolic stroke. Results- Of 1431 individuals with ischemic stroke (age, 65±15; 40% women), 323 (22.6%) had cardioembolism. AF risk was significantly associated with cardioembolism (CHA2DS2-VASc: odds ratio [OR] per SD, 1.69 [95% CI, 1.49-1.93]; Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology-AF score: OR, 2.22 [95% CI, 1.90-2.60]; electronic Health Record-Based AF: OR, 2.55 [95% CI, 2.16-3.04]). Discrimination was greater for Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology-AF score (C index, 0.695 [95% CI, 0.663-0.726]) and Electronic Health Record-Based AF score (0.713 [95% CI, 0.681-0.744]) versus CHA2DS2-VASc (C index, 0.651 [95% CI, 0.619-0.683]). Examination of AF scores across a range of thresholds indicated that AF risk may facilitate identification of individuals at low likelihood of cardioembolism (eg, negative likelihood ratios for Electronic Health Record-Based AF score ranged 0.31-0.10 at sensitivity thresholds 0.90-0.99). Conclusions- AF risk scores associate with cardioembolic stroke and exhibit moderate discrimination. Utilization of AF risk scores at the time of stroke may be most useful for identifying individuals at low probability of cardioembolism. Future analyses are warranted to assess whether stroke subtype classification can be enhanced to improve outcomes in undifferentiated stroke.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; heart; humans; odds ratio; stroke.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart S, Hart CL, Hole DJ, McMurray JJV. A population-based study of the long-term risks associated with atrial fibrillation: 20-year follow-up of the Renfrew/Paisley study. Am. J. Med. 2002;113:359–364. - PubMed
-
- Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, Hoffman EB, Deenadayalu N, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Lond. Engl 2014;383:955–962. - PubMed
-
- Sanna T, Diener H-C, Passman RS, Di Lazzaro V, Bernstein RA, Morillo CA, et al. Cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med 2014;370:2478–2486. - PubMed
-
- Gladstone DJ, Spring M, Dorian P, Panzov V, Thorpe KE, Hall J, et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med 2014;370:2467–2477. - PubMed
-
- Kishore A, Vail A, Majid A, Dawson J, Lees KR, Tyrrell PJ, et al. Detection of atrial fibrillation after ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2014;45:520–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 NS064052/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141434/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 18SFRN34110082/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- T32 HL007208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS103924/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL105780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS082285/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HL120163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS086905/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128914/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

