Cullin-7 (CUL7) is overexpressed in glioma cells and promotes tumorigenesis via NF-κB activation
- PMID: 32252802
- PMCID: PMC7132976
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-020-01553-7
Cullin-7 (CUL7) is overexpressed in glioma cells and promotes tumorigenesis via NF-κB activation
Abstract
Background: Cullin-7 (CUL7) is a member of the DOC domain-containing cullin family and is involved in the regulation of cell transformation. However, the clinical significance, potential mechanism and upstream regulators of CUL7 in malignant gliomas remain to be determined.
Methods: Expression level data and clinical information were obtained via the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, the Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas (CGGA) database, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and western blot analysis. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was used to explore the potential molecular mechanisms of CUL7. RNA silencing was performed using siRNA or lentiviral constructs in U87MG and U251 glioma cell lines and GSC267 glioma stem cells. CUL7 overexpression was performed using the GV141-CUL7 plasmid construct. In addition, overexpression of miR-3940-5p was performed and validated by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Cells were characterized in vitro or in vivo to evaluate their molecular status, cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8, EdU, flow cytometry, colony formation, Transwell and 3D tumour spheroid invasion assays. Coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) and western blotting were performed to test the mechanisms of activation of the NF-κB signalling pathway.
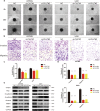
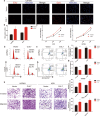
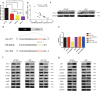
Results: High CUL7 expression was associated with a high tumour grade, a mesenchymal molecular glioma subtype and a poor prognosis in patients. Gene silencing of CUL7 in U87MG and U251 cells significantly inhibited tumour growth, invasion and migration in vitro and in vivo. Western blot analysis revealed that cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) molecular markers changed under CUL7 silencing conditions. In contrast, CUL7 overexpression promoted tumour growth, invasion and migration. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and western blot analysis revealed that CUL7 was positively associated with the NF-κB pathway. Moreover, with coimmunoprecipitation assays, we discovered that CUL7 physically associated with MST1, which further led to ubiquitin-mediated MST1 protein degradation, which promoted activation of the NF-κB signalling pathway. Finally, CUL7 was found to be downregulated by miR-3940-5p, which suppressed the development of gliomas.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that CUL7 plays a significant role in promoting tumorigenesis via NF-κB activation and that it can be negatively regulated by miR-3940-5p in human gliomas. Furthermore, CUL7 might be a candidate molecular target for the treatment of glioma.
Keywords: CUL7; Glioma; MST1; NF-κB; miR-3940-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2017CXGC1203/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China
- ZR2019BH057/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China
- 81571284/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81702468/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81874083/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

