Prognostic nomogram based on the metastatic lymph node ratio for gastric neuroendocrine tumour: SEER database analysis
- PMID: 32253246
- PMCID: PMC7174016
- DOI: 10.1136/esmoopen-2019-000632
Prognostic nomogram based on the metastatic lymph node ratio for gastric neuroendocrine tumour: SEER database analysis
Abstract
Objective: The prediction of survival of gastric neuroendocrine tumours (g-NETs) is controversial. Prognostic effects of the metastatic lymph node ratio (LNR) in patients with g-NET were explored, and a nomogram was plotted to predict the survival rates of patients.
Methods: A longitudinal study conducted on the basis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. The association between LNR and survival were investigated by using Pearson correlation and Cox regression. Overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) rates were predicted with the help of nomograms.
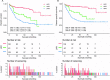
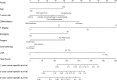
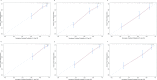
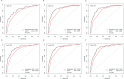
Results: A total of 315 patients with g-NET diagnosed from 2004 to 2015 were included in this study. LNR was discovered to have a negative correlation with OS and CSS (Pearson correlation coefficients: 0.343 (p<0.001) and 0.389 (p<0.001), respectively). The multivariate analyses indicated age, tumour site, differentiation, T staging, M staging, chemotherapy and LNR to be independent prognostic factors for both OS and CSS. Surgery was also a prognostic determinant for CSS (p=0.003). Concordance indices of the nomograms for OS and CSS were higher than those of the TNM classification (0.772 vs 0.730 and 0.807 vs 0.768, respectively). As per the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, predictive ability of the nomograms for survival of 1, 3 and 5 years was all better than that of TNM classification.
Conclusions: LNR is an independent predictor of g-NETs. The nomograms plotted in this study have a satisfying predictive ability of survival risks and are capable of guiding tailored treatment strategies for patients with g-NET.
Keywords: SEER database; cancer-specific survival; gastric neuroendocrine tumor; lymph node ratio; overall survival.
© Author (s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. Published by BMJ on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

