Tubule-Specific Mst1/2 Deficiency Induces CKD via YAP and Non-YAP Mechanisms
- PMID: 32253273
- PMCID: PMC7217407
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2019101052
Tubule-Specific Mst1/2 Deficiency Induces CKD via YAP and Non-YAP Mechanisms
Abstract
Background: The serine/threonine kinases MST1 and MST2 are core components of the Hippo pathway, which has been found to be critically involved in embryonic kidney development. Yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) are the pathway's main effectors. However, the biologic functions of the Hippo/YAP pathway in adult kidneys are not well understood, and the functional role of MST1 and MST2 in the kidney has not been studied.
Methods: We used immunohistochemistry to examine expression in mouse kidneys of MST1 and MST2, homologs of Hippo in Drosophila. We generated mice with tubule-specific double knockout of Mst1 and Mst2 or triple knockout of Mst1, Mst2, and Yap. PCR array and mouse inner medullary collecting duct cells were used to identify the primary target of Mst1/Mst2 deficiency.
Results: MST1 and MST2 were predominantly expressed in the tubular epithelial cells of adult kidneys. Deletion of Mst1/Mst2 in renal tubules increased activity of YAP but not TAZ. The kidneys of mutant mice showed progressive inflammation, tubular and glomerular damage, fibrosis, and functional impairment; these phenotypes were largely rescued by deletion of Yap in renal tubules. TNF-α expression was induced via both YAP-dependent and YAP-independent mechanisms, and TNF-α and YAP amplified the signaling activities of each other in the tubules of kidneys with double knockout of Mst1/Mst2.
Conclusions: Our findings show that tubular Mst1/Mst2 deficiency leads to CKD through both the YAP and non-YAP pathways and that tubular YAP activation induces renal fibrosis. The pathogenesis seems to involve the reciprocal stimulation of TNF-α and YAP signaling activities.
Keywords: CKD; Hippo; MST1; MST2; YAP; renal fibrosis.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
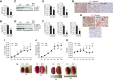
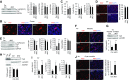
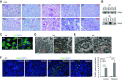
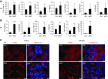
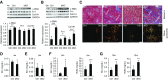
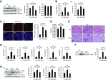
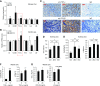
Comment in
-
Tubular MST1/2 Deletion and Renal Fibrosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 May;31(5):893-894. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020030305. Epub 2020 Apr 6. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32271714 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L, Wang W, Liu B, Liu J, et al.: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: A cross-sectional survey. Lancet 379: 815–822, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Levin A, Tonelli M, Bonventre J, Coresh J, Donner J-A, Fogo AB, et al.; ISN Global Kidney Health Summit participants: Global kidney health 2017 and beyond: A roadmap for closing gaps in care, research, and policy. Lancet 390: 1888–1917, 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

