An optimisation-based iterative approach for speckle tracking echocardiography
- PMID: 32253607
- PMCID: PMC7211789
- DOI: 10.1007/s11517-020-02142-8
An optimisation-based iterative approach for speckle tracking echocardiography
Abstract
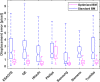
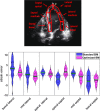
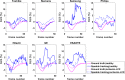
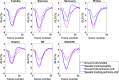
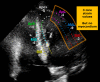
Speckle tracking is the most prominent technique used to estimate the regional movement of the heart based on echocardiograms. In this study, we propose an optimised-based block matching algorithm to perform speckle tracking iteratively. The proposed technique was evaluated using a publicly available synthetic echocardiographic dataset with known ground-truth from several major vendors and for healthy/ischaemic cases. The results were compared with the results from the classic (standard) two-dimensional block matching. The proposed method presented an average displacement error of 0.57 pixels, while classic block matching provided an average error of 1.15 pixels. When estimating the segmental/regional longitudinal strain in healthy cases, the proposed method, with an average of 0.32 ± 0.53, outperformed the classic counterpart, with an average of 3.43 ± 2.84. A similar superior performance was observed in ischaemic cases. This method does not require any additional ad hoc filtering process. Therefore, it can potentially help to reduce the variability in the strain measurements caused by various post-processing techniques applied by different implementations of the speckle tracking. Graphical Abstract Standard block matching versus proposed iterative block matching approach.
Keywords: Echocardiography; Myocardial deformation; Speckle tracking echocardiography; Strain imaging.
Figures
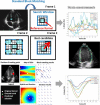

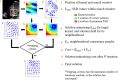
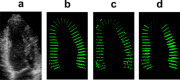
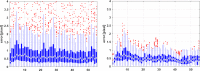
References
-
- Voigt JU, Pedrizzetti G, Lysyansky P, Marwick TH, Houle H, Baumann R, Pedri S, Ito Y, Abe Y, Metz S, Song JH. Definitions for a common standard for 2D speckle tracking echocardiography: consensus document of the EACVI/ASE/Industry Task Force to standardize deformation imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;16(1):1–11. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeu184. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barbosa D, Friboulet D, D’hooge J, Bernard O (2014) Fast tracking of the left ventricle using global anatomical affine optical flow and local recursive block matching. MIDAS J: 10
-
- Ferraiuoli P, Fixsen LS, Kappler B, Lopata RG, Fenner JW, Narracott AJ. Measurement of in vitro cardiac deformation by means of 3D digital image correlation and ultrasound 2D speckle-tracking echocardiography. Medical Engineering & Physics. 2019;74:146–152. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2019.09.021. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

