Machine Learning in Dermatology: Current Applications, Opportunities, and Limitations
- PMID: 32253623
- PMCID: PMC7211783
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-020-00372-0
Machine Learning in Dermatology: Current Applications, Opportunities, and Limitations
Abstract
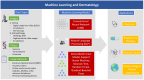
Machine learning (ML) has the potential to improve the dermatologist's practice from diagnosis to personalized treatment. Recent advancements in access to large datasets (e.g., electronic medical records, image databases, omics), faster computing, and cheaper data storage have encouraged the development of ML algorithms with human-like intelligence in dermatology. This article is an overview of the basics of ML, current applications of ML, and potential limitations and considerations for further development of ML. We have identified five current areas of applications for ML in dermatology: (1) disease classification using clinical images; (2) disease classification using dermatopathology images; (3) assessment of skin diseases using mobile applications and personal monitoring devices; (4) facilitating large-scale epidemiology research; and (5) precision medicine. The purpose of this review is to provide a guide for dermatologists to help demystify the fundamentals of ML and its wide range of applications in order to better evaluate its potential opportunities and challenges.
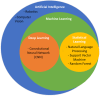
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Convolutional neural network; Deep learning; Dermatology; Image classification; Machine learning; Mobile applications; Personal monitoring devices; Precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Stephanie Chan, Vidhatha Reddy, Bridget Myers, Quinn Thibodeaux, Nicholas Brownstone have nothing to disclose. Wilson Liao is a member of the journal’s Editorial Board.
Figures