External validation of a prognostic model based on total tumor load of sentinel lymph node for early breast cancer patients
- PMID: 32253684
- PMCID: PMC7188708
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-020-05623-4
External validation of a prognostic model based on total tumor load of sentinel lymph node for early breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: A prognostic model based on the results of molecular analysis of sentinel lymph nodes (SLN) is needed to replace the information that staging the entire axilla provided. The aim of the study is to conduct an external validation of a previously developed model for the prediction of 5-year DFS in a group of breast cancer patients that had undergone SLN biopsy assessed by the One Step Nucleic Acid Amplification (OSNA) method.
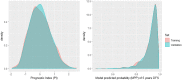
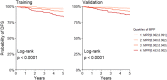
Methods: We collected retrospective data of 889 patients with breast cancer, who had not received systemic treatment before surgery, and who underwent SLN biopsy and evaluation of all SLN by OSNA. The discrimination ability of the model was assessed by the area under the ROC curve (AUC ROC), and its calibration by comparing 5-years DFS Kaplan-Meier estimates in quartile groups of model predicted probabilities (MPP).
Results: The AUC ROC ranged from 0.78 (at 2 years) to 0.73 (at 5 years) in the training set, and from 0.78 to 0.71, respectively, in the validation set. The MPP allowed to distinguish four groups of patients with heterogeneous DFS (log-rank test p < 0.0001). In the highest risk group, the HR were 6.04 [95% CI 2.70, 13.48] in the training set and 4.79 [2.310, 9.93] in the validation set.
Conclusions: The model for the prediction of 5-year DFS was successfully validated using the most stringent form of validation, in centers different from those involved in the development of the model. The external validation of the model confirms its utility for the prediction of 5-year DFS and the usefulness of the TTL value as a prognostic variable.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Model validation; Prognosis; Sentinel lymph node; Total tumor load.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Predictive and prognostic value of total tumor load in sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant treatment using one-step nucleic acid amplification: the NEOVATTL study.Clin Transl Oncol. 2021 Jul;23(7):1377-1385. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02530-4. Epub 2021 Jan 31. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33517542 Free PMC article.
-
Total tumor load assessed by one-step nucleic acid amplification assay as an intraoperative predictor for non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer.Breast. 2017 Apr;32:33-36. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.12.011. Epub 2016 Dec 25. Breast. 2017. PMID: 28030783
-
Intraoperative Nomograms, Based on One-Step Nucleic Acid Amplification, for Prediction of Non-sentinel Node Metastasis and Four or More Axillary Node Metastases in Breast Cancer Patients with Sentinel Node Metastasis.Ann Surg Oncol. 2018 Sep;25(9):2603-2611. doi: 10.1245/s10434-018-6633-0. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29978372 Free PMC article.
-
Role of total tumour load of sentinel lymph node on survival in early breast cancer patients.Breast. 2017 Jun;33:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2017.02.011. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Breast. 2017. PMID: 28254641
-
A Dutch Prediction Tool to Assess the Risk of Additional Axillary Non-Sentinel Lymph Node Involvement in Sentinel Node-Positive Breast Cancer Patients.Clin Breast Cancer. 2016 Apr;16(2):123-30. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2015.09.003. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Clin Breast Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26602438
Cited by
-
Predictive and prognostic value of total tumor load in sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant treatment using one-step nucleic acid amplification: the NEOVATTL study.Clin Transl Oncol. 2021 Jul;23(7):1377-1385. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02530-4. Epub 2021 Jan 31. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33517542 Free PMC article.
-
Total Tumor Load of mRNA Cytokeratin 19 in the Sentinel Lymph Node as a Predictive Value of Axillary Lymphadenectomy in Patients with Neoadjuvant Breast Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jan 8;12(1):77. doi: 10.3390/genes12010077. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33435629 Free PMC article.
-
Using population-based data to evaluate the impact of adherence to endocrine therapy on survival in breast cancer through the web-application BreCanSurvPred.Sci Rep. 2022 May 16;12(1):8097. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12228-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35577853 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of prognostic and predictive value of total tumoral load after primary systemic therapy in breast cancer using OSNA assay.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 May;26(5):1220-1228. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03347-7. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38070048 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Detection of Lymph Node Metastases with One-Step Nucleic Acid Amplification (OSNA) Pooling in Prostate Cancer: The POPCORN Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 17;25(24):13489. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413489. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769252 Free PMC article.

