Functionalization of Alginate with Extracellular Matrix Peptides Enhances Viability and Function of Encapsulated Porcine Islets
- PMID: 32255552
- PMCID: PMC7598935
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202000102
Functionalization of Alginate with Extracellular Matrix Peptides Enhances Viability and Function of Encapsulated Porcine Islets
Abstract
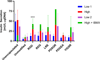
Translation of transplanted alginate-encapsulated pancreatic islets to treat type 1 diabetes has been hindered by inconsistent long-term efficacy. This loss of graft function can be partially attributed to islet dysfunction associated with the destruction of extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions during the islet isolation process as well as immunosuppression-associated side effects. This study aims at recapitulating islet-ECM interactions by the direct functionalization of alginate with the ECM-derived peptides RGD, LRE, YIGSR, PDGEA, and PDSGR. Peptide functionalization is controlled in a concentration-dependent manner and its presentation is found to be homogeneous across the microcapsule environment. Preweaned porcine islets are encapsulated in peptide-functionalized alginate microcapsules, and those encapsulated in RGD-functionalized alginate displays enhanced viability and glucose-stimulated insulin release. Effects are RGD-specific and not observed with its scrambled control RDG nor with LRE, YIGSR, PDGEA, and PDSGR. This study supports the sustained presentation of ECM-derived peptides in helping to maintain health of encapsulated pancreatic islets and may aid in prolonging longevity of encapsulated islet grafts.
Keywords: alginate; cell encapsulation; encapsulated pancreatic islets; type 1 diabetes.
© 2020 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- de Vos P, Lazarjani HA, Poncelet D, Faas MM; Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 2014, 68, 15. - PubMed
-
- Orive G, Hernandez RM, Gascon AR, Calafiore R, Chang TMS, de Vos P, Hortelano G, Hunkeler D, Lacik I, Shapiro AM, Pedraz JL; Nat. Med 2003, 9, 104. - PubMed
-
- Leijs M, Villafuertes E, Haeck J, Koevoet W, Fernandez-Gutierrez B, Hoogduijn M, Verhaar J, Bernsen M, van Buul G, van Osch G; Eur. Cell. Mater 2017, 33, 43. - PubMed
-
- Zhao X, Liu S, Yildirimer L, Zhao H, Ding R, Wang H, Cui W, Weitz D; Adv. Funct. Mater 2016, 26, 2809.

