Learning from amyloid trials in Alzheimer's disease. A virtual patient analysis using a quantitative systems pharmacology approach
- PMID: 32255562
- PMCID: PMC7983876
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.12082
Learning from amyloid trials in Alzheimer's disease. A virtual patient analysis using a quantitative systems pharmacology approach
Abstract
Background: Many trials of amyloid-modulating agents fail to improve cognitive outcome in Alzheimer's disease despite substantial reduction of amyloid β levels.
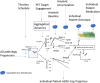
Methods: We applied a mechanism-based Quantitative Systems Pharmacology model exploring the pharmacodynamic interactions of apolipoprotein E (APOE), Catechol -O -methyl Transferase (COMTVal158Met), and 5-HT transporter (5-HTTLPR) rs25531 genotypes and aducanumab.
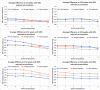
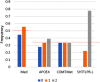
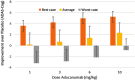
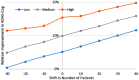
Results: The model predicts large clinical variability. Anticipated placebo differences on Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS)-COG in the aducanumab ENGAGE and EMERGE ranged from 0.77 worsening to 1.56 points improvement, depending on the genotype-comedication combination. 5-HTTLPR L/L subjects are found to be the most resilient. Virtual patient simulations suggest improvements over placebo between 4% and 20% at the 10 mg/kg dose, depending on the imbalance of the 5-HTTLPR genotype and exposure. In the Phase II PRIME trial, maximal anticipated placebo difference at 10 mg/kg ranges from 0.3 worsening to 5.3 points improvement.
Discussion: These virtual patient simulations, once validated against clinical data, could lead to better informed future clinical trial designs.
Keywords: aducanumab; genotype; medication; pharmacodynamic effect; responder profile.
© 2020 In Silico Biosciences. Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
At the time of the study, the authors were employees of In Silico Biosciences. HG is now with Certara‐QSP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simulating the Effects of Common Comedications and Genotypes on Alzheimer's Cognitive Trajectory Using a Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Approach.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;78(1):413-424. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200688. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 33016912
-
Genetic correlates of behavioral endophenotypes in Alzheimer disease: role of COMT, 5-HTTLPR and APOE polymorphisms.Neurobiol Aging. 2006 Nov;27(11):1595-603. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.09.029. Epub 2005 Oct 27. Neurobiol Aging. 2006. PMID: 16257094
-
Cumulative effect of COMT and 5-HTTLPR polymorphisms and their interaction with disease severity and comorbidities on the risk of psychosis in Alzheimer disease.Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2006 Apr;14(4):343-51. doi: 10.1097/01.JGP.0000192491.50802.c3. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16582043
-
Aducanumab: First Approval.Drugs. 2021 Aug;81(12):1437-1443. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01569-z. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34324167 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's disease: an update.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2014;37:79-100. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-071013-014300. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24821312 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarker changes associated with fornix deep brain stimulation in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jun;21(6):e70394. doi: 10.1002/alz.70394. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 40566800 Free PMC article.
-
Hallmarks of neurodegenerative disease: A systems pharmacology perspective.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2022 Nov;11(11):1399-1429. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12852. Epub 2022 Aug 17. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35894182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Approaches for Supporting Combination Therapy in the Post-Aducanumab Era in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2021 Nov 23;5(1):815-826. doi: 10.3233/ADR-210039. eCollection 2021. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2021. PMID: 34966890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A modeling informed quantitative approach to salvage clinical trials interrupted due to COVID-19.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2020 Nov 2;6(1):e12053. doi: 10.1002/trc2.12053. eCollection 2020. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2020. PMID: 33163611 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of clinical failure of anti-tau and anti-synuclein antibodies in neurodegeneration using a quantitative systems pharmacology model.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 1;13(1):14342. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41382-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37658103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foroutan N, Hopkins RB, Tarride JE, Florez ID, Levine M. Safety and efficacy of active and passive immunotherapy in mild‐to‐moderate Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Clin Invest Med. 2019;42:E53‐E65. - PubMed
-
- Penninkilampi R, Brothers HM, Eslick GD. Safety and Efficacy of Anti‐Amyloid‐beta immunotherapy in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017;12:194‐203. - PubMed
-
- Aisen PS, Siemers E, Michelson D, et al. What have we learned from expedition III and EPOCH trials? Perspective of the CTAD task force. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2018;5:171‐174. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

