Intercalated cell BKα subunit is required for flow-induced K+ secretion
- PMID: 32255763
- PMCID: PMC7205426
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.130553
Intercalated cell BKα subunit is required for flow-induced K+ secretion
Abstract
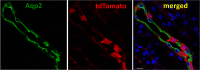
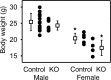
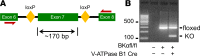
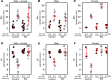
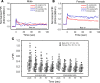
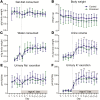
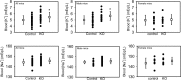
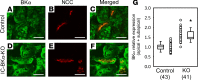
BK channels are expressed in intercalated cells (ICs) and principal cells (PCs) in the cortical collecting duct (CCD) of the mammalian kidney and have been proposed to be responsible for flow-induced K+ secretion (FIKS) and K+ adaptation. To examine the IC-specific role of BK channels, we generated a mouse with targeted disruption of the pore-forming BK α subunit (BKα) in ICs (IC-BKα-KO). Whole cell charybdotoxin-sensitive (ChTX-sensitive) K+ currents were readily detected in control ICs but largely absent in ICs of IC-BKα-KO mice. When placed on a high K+ (HK) diet for 13 days, blood [K+] was significantly greater in IC-BKα-KO mice versus controls in males only, although urinary K+ excretion rates following isotonic volume expansion were similar in males and females. FIKS was present in microperfused CCDs isolated from controls but was absent in IC-BKα-KO CCDs of both sexes. Also, flow-stimulated epithelial Na+ channel-mediated (ENaC-mediated) Na+ absorption was greater in CCDs from female IC-BKα-KO mice than in CCDs from males. Our results confirm a critical role of IC BK channels in FIKS. Sex contributes to the capacity for adaptation to a HK diet in IC-BKα-KO mice.
Keywords: Cell Biology; Epithelial transport of ions and water; Ion channels; Mouse models; Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
PIEZO1 is a distal nephron mechanosensor and is required for flow-induced K+ secretion.J Clin Invest. 2024 Mar 1;134(5):e174806. doi: 10.1172/JCI174806. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38426496 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanosensitive BKα/β1 channel localizes to cilia of principal cells in rabbit cortical collecting duct (CCD).Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;312(1):F143-F156. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00256.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27806944 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NKCC in BK channel-mediated net K⁺ secretion in the CCD.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Nov;301(5):F1088-97. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00347.2011. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21816753 Free PMC article.
-
An unexpected journey: conceptual evolution of mechanoregulated potassium transport in the distal nephron.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Feb 15;310(4):C243-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00328.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26632600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Going with the flow: New insights regarding flow induced K+ secretion in the distal nephron.Physiol Rep. 2024 Oct;12(20):e70087. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70087. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39428258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The transcription factor Foxi1 promotes expression of V-ATPase and Gpr116 in M-1 cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Mar 1;324(3):F267-F273. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00272.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36603001 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating the kidney organoid: insights into assessment and enhancement of nephron function.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Dec 1;325(6):F695-F706. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00166.2023. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37767571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rare Variants in Genes Encoding Subunits of the Epithelial Na+ Channel Are Associated With Blood Pressure and Kidney Function.Hypertension. 2022 Nov;79(11):2573-2582. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18513. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 36193739 Free PMC article.
-
PIEZO1 is a distal nephron mechanosensor and is required for flow-induced K+ secretion.J Clin Invest. 2024 Mar 1;134(5):e174806. doi: 10.1172/JCI174806. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38426496 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Differences in Kidney Function and Blood Pressure Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 8;25(16):8637. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168637. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201324 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frindt G, Palmer LG. Low-conductance K channels in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1989;256(1 Pt 2):F143–F151. - PubMed
-
- Satlin LM, Palmer LG. Apical K+ conductance in maturing rabbit principal cell. Am J Physiol. 1997;272(3 Pt 2):F397–F404. - PubMed
-
- Wang WH, Schwab A, Giebisch G. Regulation of small-conductance K+ channel in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1990;259(3 Pt 2):F494–F502. - PubMed
-
- Xu JZ, Hall AE, Peterson LN, Bienkowski MJ, Eessalu TE, Hebert SC. Localization of the ROMK protein on apical membranes of rat kidney nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1997;273(5):F739–F748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

