Sex Differences in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis: A Comprehensive Study Based on Bioinformatics
- PMID: 32255771
- PMCID: PMC7163332
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.923331
Sex Differences in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis: A Comprehensive Study Based on Bioinformatics
Abstract
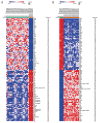
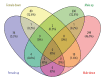
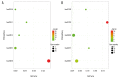
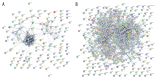
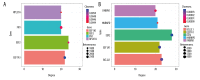
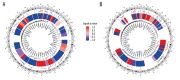
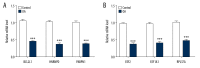
BACKGROUND Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common disorder in the elderly. OA influences the daily life of patients and has become a worldwide health problem. It is still unclear whether the pathogenesis mechanism is different between males and females. This study investigated the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and explored the different signaling pathways of OA between males and females. MATERIAL AND METHODS Data sets of GSE55457, GSE55584, and GSE12021 were retrieved from Gene Expression Omnibus to conduct DEGs analysis. Enrichment analysis of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway and Gene Ontology term was performed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) bioinformatics tool. The protein interaction network was constructed in Cytoscape 3.7.2. qRT-PCR was then performed to validate the expression of hub genes in OA patients and healthy people. RESULTS In total, 4 co-upregulated and 10 co-downregulated genes were identified. We found that enriched pathways were different between males and females. BCL2L1, EEF1A1, EEF2, HNRNPD, and PABPN1 were considered as hub genes in OA pathogenesis in males, while EEF2, EEF1A1, RPL37A, FN1 were considered as hub genes in OA pathogenesis in females. Consistent with the bioinformatics analysis, the qRT-PCR analysis also showed that the gene expression of BCL2L1, HNRNPD, and PABPN1 was significantly lower in male OA patients. In contrast, EEF2, EEF1A1, and RPL37A were significantly lower in female OA patients. CONCLUSIONS The DEGs identified may be involved in different OA disease progression mechanisms between males and females, and they are considered as treatment targets or prognosis markers for males and females. The pathogenesis mechanism is sex-dependent.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

