Influence of interferon-based drugs on immunological indices in specific prevention
- PMID: 32255964
- PMCID: PMC7096290
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2020.238-244
Influence of interferon-based drugs on immunological indices in specific prevention
Abstract
Aim: The research aimed to study the effect of interferon (IFN)-based drugs on the behavior of immunological parameters in calves during the specific prevention of associative infections.
Materials and methods: The object of research was 45 black motley cows and their calves from birth to 2 months of life. Serum and colostrum samples were screened for antibodies against Rotavirus, diarrhea, and coronavirus using serological methods. The testing was performed before vaccination, 40 days before calving, 20 days before calving, and before calving. Colostrum samples were taken during the first milk yield. Serum samples from calves were drawn before colostrum feeding as well as at 7, 14, and 21 days, and 1 and 2 months of age. To measure the level of immunoglobulins A, M, and G, additional serum samples were collected from calves at 25, 35, 65, and 75 days after birth.
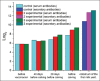
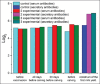
Results: Giving pregnant cows, an IFN-based drug at a dose of 1 ml/kg 48 h before vaccination results in the development and accumulation of antibodies to Rotavirus, coronavirus, and viral diarrhea (VD) in the colostrum, with a titer of 7.6±0.3 log2, 5.8±0.34 log2, and 4.4±0.18 log2, respectively. It indicates an increase in the antigenic activity of the multivalent vaccine.
Conclusion: IFN-based drugs enhance the protective effect of vaccination against associative infections in the newborn calves. They stimulate a rise in the titer of antibodies to Rotavirus, coronavirus, VD, and mucosal disease complex as well as an increase in immunoglobulins A, M, and G.
Keywords: Rotavirus; antibody titer; coronavirus; immunoglobulins A, M, and G; interferon; vaccinations.
Copyright: © Andreeva, et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serological, colostral and milk responses of cows vaccinated with a single dose of a combined vaccine against rotavirus, coronavirus and Escherichia coli F5 (K99).Vet Rec. 2001 Jul 28;149(4):105-8. doi: 10.1136/vr.149.4.105. Vet Rec. 2001. PMID: 11504200
-
Field trial evaluation of an inactivated rotavirus vaccine against neonatal diarrhea of calves.Eur J Epidemiol. 1987 Mar;3(1):5-9. doi: 10.1007/BF00145064. Eur J Epidemiol. 1987. PMID: 3034660 Free PMC article.
-
Passive immunity to bovine rotavirus in newborn calves fed colostrum supplements from immunized or nonimmunized cows.Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1118-31. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1118-1131.1983. Infect Immun. 1983. PMID: 6309660 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal and systemic antibody responses to bovine coronavirus structural proteins in experimentally challenge-exposed calves fed low or high amounts of colostral antibodies.Am J Vet Res. 1991 May;52(5):700-8. Am J Vet Res. 1991. PMID: 1649563
-
The efficacy of colostrum from cows vaccinated with rotavirus in protecting calves to experimentally induced rotavirus infection.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984;7(1):11-8. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(84)90011-0. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984. PMID: 6086224
Cited by
-
Efficiency of high-carbohydrate fodder in the diets of Holstein cows.Vet World. 2021 May;14(5):1303-1310. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2021.1303-1310. Epub 2021 May 25. Vet World. 2021. PMID: 34220135 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory effect of the combined use of Vetosporin Zh probiotic and Gumi-malysh biologically active additive.Vet World. 2021 Jul;14(7):1915-1921. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2021.1915-1921. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Vet World. 2021. PMID: 34475717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khaziahmetov F, Khabirov A, Avzalov R, Tsapalova G, Tagirov K, Giniyatullin S, Andreeva A, Gafarova F, Gafarov F. Effects of Paenibacillus-based probiotic (bacispecin) on growth performance, gut microflora and hematology indices in goslings. J. Eng. Appl. 2018;13(8):6541–6545.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
