On the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Genomics to Enhance Precision Medicine
- PMID: 32256101
- PMCID: PMC7090191
- DOI: 10.2147/PGPM.S205082
On the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Genomics to Enhance Precision Medicine
Abstract
The complexity of orphan diseases, which are those that do not have an effective treatment, together with the high dimensionality of the genetic data used for their analysis and the high degree of uncertainty in the understanding of the mechanisms and genetic pathways which are involved in their development, motivate the use of advanced techniques of artificial intelligence and in-depth knowledge of molecular biology, which is crucial in order to find plausible solutions in drug design, including drug repositioning. Particularly, we show that the use of robust deep sampling methodologies of the altered genetics serves to obtain meaningful results and dramatically decreases the cost of research and development in drug design, influencing very positively the use of precision medicine and the outcomes in patients. The target-centric approach and the use of strong prior hypotheses that are not matched against reality (disease genetic data) are undoubtedly the cause of the high number of drug design failures and attrition rates. Sampling and prediction under uncertain conditions cannot be avoided in the development of precision medicine.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; big data; drug design; genomics; precision medicine.
© 2020 Álvarez-Machancoses et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
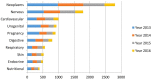
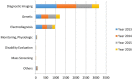
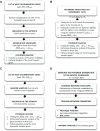
References
-
- Becker A. Artificial intelligence in medicine: what is it doing for us today? Health Policy Technol. 2019;8:198–205. doi: 10.1016/j.hlpt.2019.03.004 - DOI
-
- Mesko B. The role of artificial intelligence in precision medicine. Expert Rev Precis Med Drug Develop. 2017;2:239–241. doi: 10.1080/23808993.2017.1380516 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

