Establishment of Simple Nomograms for Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Involvement in Early Breast Cancer
- PMID: 32256110
- PMCID: PMC7090154
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S241641
Establishment of Simple Nomograms for Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Involvement in Early Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Axillary lymph node (ALN) involvement is an important prognostic factor of early invasive breast cancer. The objective of this study was to establish simple nomograms for predicting ALN involvement based on ultrasound (US) characteristics and evaluate the predictive value of US in the detection of ALN involvement.
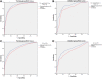
Patients and methods: A total of 1328 patients with cT1-2N0 breast cancer by physical exam were retrospectively analyzed. Univariate analysis was used for the comparison of variables, and multivariate analysis was performed by binary logistic regression analysis. The R software was used to establish simple nomograms based on the US characteristics alone. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of the prediction model and the verification group were drawn, and the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated to evaluate the discrimination of the prediction model. A calibration curve was plotted to assess the nomogram predictions vs the actual observations of the ALN metastasis rate and axillary tumor burden rate.
Results: The ALN metastasis rates of the training group and the validation group were 35.1% and 34.1%, respectively. Multivariate analysis showed that molecular subtype, lymphovascular invasion, mass descriptors (size, margin, microcalcification and blood flow signal) and LN descriptors (shape, cortical thickness and long-to-short ratio) were independent impact factors in early breast cancer. The AUC of ALN metastasis rate of prediction model based on US features was 0.802, the AUC of high tumor burden rate was 0.873, and the AUC of external validation group was 0.731 and 0.802, respectively. The calibration curve of the nomogram showed that the nomogram predictions are consistent with the actual metastasis rate and the high tumor burden rate. The results showed that preoperative US had a sensitivity of 59.4% and a specificity of 88.9% for predicting the ALN metastasis rate.
Conclusion: The successfully established nomograms based on US characteristics to predict ALN metastasis rate and high axillary tumor burden rate in early breast cancer can achieve individual prediction. Compared with other nomogram predictions, it is more intuitive, and can help clinical decision-making; thus, it should be promoted. However, at this time US features alone are insufficient to replace sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Keywords: axillary lymph node involvement; early breast cancer; nomogram; ultrasound.
© 2020 Zong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preoperative prediction of axillary sentinel lymph node burden with multiparametric MRI-based radiomics nomogram in early-stage breast cancer.Eur Radiol. 2021 Aug;31(8):5924-5939. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07674-z. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33569620
-
Predicting the risk of axillary lymph node metastasis in early breast cancer patients based on ultrasonographic-clinicopathologic features and the use of nomograms: a prospective single-center observational study.Eur Radiol. 2022 Dec;32(12):8200-8212. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08855-8. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 36169686
-
Nomogram models for stratified prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients (cN0).Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 30;13:967062. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.967062. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36111297 Free PMC article.
-
Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS)-based radiomics nomogram: an individualized tool for predicting axillary lymph node tumor burden in patients with early breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2023 Apr 13;23(1):340. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10743-3. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37055722 Free PMC article.
-
Mammography-based radiomics nomogram: a potential biomarker to predict axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer.Br J Radiol. 2020 Jul;93(1111):20191019. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20191019. Epub 2020 May 27. Br J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32401540 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Status With a Nomogram Based on Breast Lesion Ultrasound Features: Performance in N1 Breast Cancer Patients.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 27;10:581321. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.581321. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194714 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative prediction of HER2 expression and sentinel lymph node status in breast cancer using a mammography radiomics model.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 4;15:1578458. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1578458. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40535132 Free PMC article.
-
Development of High-Resolution Dedicated PET-Based Radiomics Machine Learning Model to Predict Axillary Lymph Node Status in Early-Stage Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 14;14(4):950. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040950. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205699 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal treatment strategy for hormone receptor-positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer patients with 1-2 suspicious axillary lymph node metastases on breast magnetic resonance imaging: upfront surgery vs. neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Front Oncol. 2023 May 17;13:936148. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.936148. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37265793 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive factors of axillary lymph node involvement in Tunisian women with early breast cancer.Afr Health Sci. 2023 Dec;23(4):275-283. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v23i4.30. Afr Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 38974280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(10):918–926. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.11470 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chue KM, Yong WS, Thike AA, et al. Predicting the likelihood of additional lymph node metastasis in sentinel lymph node positive breast cancer: validation of the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Centre (MSKCC) nomogram. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67(2):112–119. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2013-201524 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

