Acute Effects of 2C-E in Humans: An Observational Study
- PMID: 32256350
- PMCID: PMC7093582
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00233
Acute Effects of 2C-E in Humans: An Observational Study
Abstract
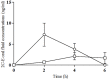
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylphenethylamine (2C-E) is psychedelic phenylethylamine, with a chemical structure similar to mescaline, used as new psychoactive substance (NPS). It inhibits norepinephrine and serotonin uptake and, more relevant, acts as a partial agonist of the serotonin 2A (5-HT2 A), 2B (5-HT2 B), and (5-HT2 C) receptors. Consumers have reported that 2C-E induces mild-moderate psychedelic effects, but its pharmacology in humans, including pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics, have not yet studied. To assess the acute effects of 2C-E on physiological and subjective effects and evaluate its pharmacokinetics, an observational study was carried-out. Ten recreational users of psychedelics self-administered a single oral dose of 2C-E (6.5, 8, 10, 15, or 25 mg). Blood pressure and heart rate were evaluated at baseline, 2, 4, and 6 h post-administration. Three rating scales were administered to evaluate subjective effects: a set of Visual Analog Scales (VAS), the 49-item short form version of the Addiction Research Centre Inventory (ARCI), and the Evaluation of the Subjective Effects of Substances with Abuse Potential (VESSPA-SSE) at baseline, 2, 4, and 6 h after self-administration. To assess 2C-E concentrations oral fluid (saliva) was collected during 6 h. 2C-E induced primarily alterations in perceptions, hallucinations, and euphoric-mood. Saliva maximal concentrations were achieved 2 h after self-administration. Administration of oral 2C-E at recreational doses produces a group of psychedelic-like effects such to 2C-B and other serotonin-acting drugs.
Keywords: 2C-E (2; 5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylphenethylamine); novel psychoactive substances (NPS); phenylethylamines; psychedelic; psychostimulants.
Copyright © 2020 Papaseit, Olesti, Pérez-Mañá, Torrens, Grifell, Ventura, Pozo, de Sousa Fernandes Perna, Ramaekers, de la Torre and Farré.
Figures


References
-
- Cami J., Farré M., Mas M., Roset P. N., Poudevida S., Mas A., et al. (2000). ). Human pharmacology of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (“ecstasy”): psychomotor performance and subjective effects. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 20 455–466. - PubMed
-
- Caudevilla-Gálligo F., Riba J., Ventura M., González D., Farré M., Barbanoj M. J., et al. (2012). 4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B): presence in the recreational drug market in Spain, pattern of use and subjective effects. J. Psychopharmacol. 26 1026–1035. 10.1177/0269881111431752 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

