The Genomic Context for the Evolution and Transmission of Community-Associated Staphylococcus aureus ST59 Through the Food Chain
- PMID: 32256477
- PMCID: PMC7090029
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00422
The Genomic Context for the Evolution and Transmission of Community-Associated Staphylococcus aureus ST59 Through the Food Chain
Abstract
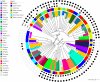
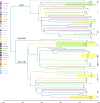
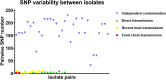
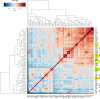
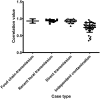
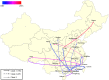
Sequence type 59 (ST59) is a predominant clonal lineage of community-acquired, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) in Asia. Despite its increasing clinical relevance in China, the evolution and geographic expansion of ST59 has been relatively uncared for. Previous study has shown that ST59 was the predominant clone in food-related MRSA in China. This study compared the genomes of 87 clonal complex (CC) 59 S. aureus isolates sourced from food chain and infection cases to reconstruct the molecular evolution and geographical spread of ST59. Accordingly, three major sub-clades of ST59 were identified and these did not correlate with isolation source or location. Phylogenetic analysis estimated that ST59 in mainland China diverged from a most common recent ancestor around 1974, and most of the cases of cross-country transmission occurred between 1987 and 2000. Notably, two recent events of cross-country transmission through the food chain were observed, the isolates from these events diverged within relatively short time intervals. These isolates also showed high similarity in terms of their core genome, accessory genes, and antibiotic resistance patterns. These findings provide a valuable insight into the potential route of ST59 expansion in China and indicate a need for robust food chain surveillance to prevent the spread of this pathogen.
Keywords: ST59 lineage; Staphylococcus aureus; food chain; molecular evolution; transmission.
Copyright © 2020 Pang, Wu, Zhang, Huang, Wu, Zhang, Li, Ding, Zhang, Chen, Wei, Zhang, Gu, Zhou, Liang, Li and Wu.
Figures
References
-
- Abulreesh H. H. (2011). “Multidrug-resistant staphylococci in the environment,” in Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Biotechnology and Environment Management. Singapore.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

