Long-Term Delivery of an Anti-SIV Monoclonal Antibody With AAV
- PMID: 32256496
- PMCID: PMC7089924
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00449
Long-Term Delivery of an Anti-SIV Monoclonal Antibody With AAV
Abstract
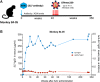
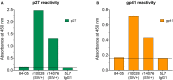
Long-term delivery of anti-HIV monoclonal antibodies using adeno-associated virus (AAV) holds promise for the prevention and treatment of HIV infection. We previously reported that after receiving a single administration of AAV vector coding for anti-SIV antibody 5L7, monkey 84-05 achieved high levels of AAV-delivered 5L7 IgG1 in vivo which conferred sterile protection against six successive, escalating dose, intravenous challenges with highly infectious, highly pathogenic SIVmac239, including a final challenge with 10 animal infectious doses (1). Here we report that monkey 84-05 has successfully maintained 240-350 μg/ml of anti-SIV antibody 5L7 for over 6 years. Approximately 2% of the circulating IgG in this monkey is this one monoclonal antibody. This monkey generated little or no anti-drug antibodies (ADA) to the AAV-delivered antibody for the duration of the study. Due to the nature of the high-dose challenge used and in order to rule out a potential low-level infection not detected by regular viral loads, we have used ultrasensitive techniques to detect cell-associated viral DNA and RNA in PBMCs from this animal. In addition, we have tested serum from 84-05 by ELISA against overlapping peptides spanning the whole envelope sequence for SIVmac239 (PepScan) and against recombinant p27 and gp41 proteins. No reactivity has been detected in the ELISAs indicating the absence of naturally arising anti-SIV antibodies; moreover, the ultrasensitive cell-associated viral tests yielded no positive reaction. We conclude that macaque 84-05 was effectively protected and remained uninfected. Our data show that durable, continuous antibody expression can be achieved after one single administration of AAV and support the potential for lifelong protection against HIV from a single vector administration.
Keywords: AAV vector; HIV/SIV cure; broadly neutralizing antibodies; gene therapy; immunotherapy; long-term expression; prophylaxis; rhesus monkeys.
Copyright © 2020 Martinez-Navio, Fuchs, Mendes, Rakasz, Gao, Lifson and Desrosiers.
Figures

References
-
- FDA U.S. Food and Drug Administration - What is Gene Therapy? (2018). Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/cellular-gene-therapy-produ...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

