PD-1-Mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Caspase 9/Caspase 3 and ERK Pathways Are Involved in Regulating the Apoptosis and Proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells During BVDV Infection in vitro
- PMID: 32256500
- PMCID: PMC7089960
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00467
PD-1-Mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Caspase 9/Caspase 3 and ERK Pathways Are Involved in Regulating the Apoptosis and Proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells During BVDV Infection in vitro
Abstract
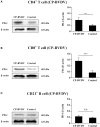
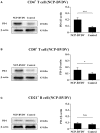
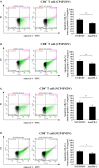
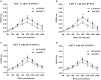
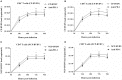
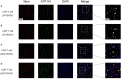
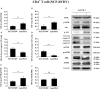
Acute infection of bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) is associated with immune dysfunction and can cause peripheral blood lymphopenia and lymphocyte apoptosis. Our previous study has confirmed that programmed death-1 (PD-1) blockade inhibits peripheral blood lymphocyte (PBL) apoptosis and restores proliferation and anti-viral immune functions of lymphocytes after BVDV infection in vitro. However, the immunomodulatory effects of PD-1 pathway on major PBL subsets are unclear and their underlying molecular mechanisms need to be further studied. Therefore, in this study, we examined PD-1 expression in bovine PBL subsets after BVDV infection in vitro and analyzed the effects of PD-1 blockade on the apoptosis and proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and expression of PD-1 downstream signaling molecules. The results showed that PD-1 expression was enhanced on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, but not on CD21+ B cells after cytopathic (CP) BVDV (strain NADL) and non-cytopathic (NCP) BVDV (strain KD) infection in vitro and PD-1 blockade significantly reduced the apoptosis of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after these two strains infection. Remarkably, PD-1 blockade significantly increased the proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after CP BVDV infection, but only significantly increased the proliferation of CD4+ T cells after NCP BVDV infection. In addition, we confirmed that PD-1-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR, caspase 9/caspase 3 and ERK pathways are involved in regulating the apoptosis and proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells during BVDV infection in vitro. Notably, ERK is involved in the regulation mechanism PD-1 mediated only when the cells are infected with CP BVDV. Our findings provide a scientific basis for exploring the molecular mechanism of immune dysfunction caused by acute BVDV infection.
Keywords: PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway; bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV); immune dysfunction; lymphocyte; programmed death-1 (PD-1).
Copyright © 2020 Liu, Liu, Wu, Huang, Xu, Lian, Wang, Yue, Chen and Zhu.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

