Mapping of developmental dysplasia of the hip to two novel regions at 8q23-q24 and 12p12
- PMID: 32256763
- PMCID: PMC7086185
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.8513
Mapping of developmental dysplasia of the hip to two novel regions at 8q23-q24 and 12p12
Abstract
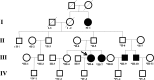
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), previously known as congenital hip dislocation, is a frequently disabling condition characterized by premature arthritis later in life. Genetic factors play a key role in the aetiology of DDH. In the present study, a genome-wide linkage scan with the Affymetrix 10K GeneChip was performed on a four-generation Chinese family, which included 19 healthy members and 5 patients. Parametric and non-parametric multipoint linkage analyses were carried out with Genespring GT v.2.0 software, and the logarithm of odds (LOD) score and nonparametric linkage (NPL) score were calculated. Parametric linkage analysis was performed, assuming an autosomal recessive trait with full penetrance and Affymetrix 'Asian' allele frequencies. The strongest evidence for linkage was found on chromosome 8q23-24, with a peak LOD score of 2.658 (θ=0), covering 2.377 Mb from single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs724717 to rs720132. This interval included nine additional successive SNPs: rs1566071, rs1902121, rs756404, rs702768, rs777813, rs2033995, rs147959, rs2884367 and rs1898287. The same region also yielded the highest NPL score of 2.883 (P=0.0156) from the non-parametric multipoint linkage analysis. Additionally, the second highest NPL score of 2.727 (P=0.0156) and LOD score of 2.528 (θ=0) were obtained on chromosome 12p12 for three consecutive markers (rs1919980, rs763853 and rs725124). This region overlapped a narrow distance of 0.642 Mb. Notably, in addition to these two regions; no significant linkage was identified for other chromosomal regions (with LOD and NPL scores >2.0). For the first time, at least for this pedigree, the evidence in the present study showed that DDH is mapped to two novel regions at 8q23-q24 and 12p12.
Keywords: developmental dysplasia of the hip; gene mapping; linkage; microarray chip; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures


References
-
- Benson MKD. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: Early diagnosis and management. Curr Paediatr. 1996;6:2–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
