High expression of FOXO3 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 32256814
- PMCID: PMC7074409
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.11430
High expression of FOXO3 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
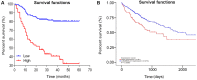
The role of forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) as a tumor suppressor gene and its association with the human lifespan is well documented. However, several studies have indicated that high expression of FOXO3 is also significantly associated with tumorigenesis. The aim of the present study was to determine the clinical significance of FOXO3 in the development and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). mRNA expression data of FOXO3 from The Cancer Genome Atlas database was analyzed through the UALCAN online tool to compare the expression of FOXO3 between HCC and normal liver tissues. Subsequently, the expression of FOXO3 at the protein level was investigated via immunohistochemical staining of 314 HCC and 150 non-cancerous liver tissue samples. The association between protein expression and clinicopathological parameters was analyzed using the χ2 test, and the effect of FOXO3 expression on survival was assessed via Kaplan-Meier analysis. The expression of FOXO3 mRNA was significantly higher in HCC in comparison with healthy tissues. High FOXO3 protein expression was revealed in 43/150 non-cancerous liver tissues, and in 238/314 HCC samples. A significant association was demonstrated between FOXO3 expression and metastasis, Tumor-Node-Metastasis stage, Edmondson grade, α-fetoprotein level and overall survival. In conclusion, the high expression of FOXO3 predicts a poor prognosis in patients with HCC, indicating this protein as a potential therapeutic target in HCC.
Keywords: forkhead box O3; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright: © Song et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Association of FOXO3 Expression with Tumor Pathogenesis, Prognosis and Clinicopathological Features in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 26;13(21):5349. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215349. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlations of Foxo3 and Foxo4 expressions with clinicopathological features and prognosis of bladder cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2017 Jul;213(7):766-772. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.04.004. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2017. PMID: 28554751
-
Identification of a novel FOXO3‑associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2025 Mar 13;29(5):230. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.14976. eCollection 2025 May. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40114746 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoskeleton-associated membrane protein 4 is upregulated in tumor tissues and is associated with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2020 Jun;19(6):3889-3898. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11499. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32382336 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Forkhead Box O Proteins in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Biology and Progression (Review).Front Oncol. 2021 May 27;11:667730. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.667730. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34123834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 8;9(11):1639. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111639. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOXO3-induced lncRNA LOC554202 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the miR-485-5p/BSG axis.Cancer Gene Ther. 2022 Mar;29(3-4):326-340. doi: 10.1038/s41417-021-00312-w. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022. PMID: 33654226 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO3a and Its Regulators in Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 20;22(22):12530. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212530. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy-Related Chemoprotection against Sorafenib in Human Hepatocarcinoma: Role of FOXO3 Upregulation and Modulation by Regorafenib.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 29;22(21):11770. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111770. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769197 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular subtypes and scoring tools related to Foxo signaling pathway for assessing hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis and treatment responsiveness.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 24;14:1213506. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1213506. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37693891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration. Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, Allen C, Al-Raddadi R, Alvis-Guzman N, Amoako Y, et al. The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the global, regional, and national level: Results From the global burden of disease study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1683–1691. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network, corp-author. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN guidelines): Hepatobiliary cancers (version 2.2016) https://www.nccn.org/about/news/ebulletin/ebulletindetail.aspx?ebulletin.... [Jun 27;2016 ];2016
-
- Samji H, Yu A, Kuo M, Alavi M, Woods R, Alvarez M, Dore GJ, Tyndall M, Krajden M, Janjua NZ, BC Hepatitis Testers Cohort Team Late hepatitis B and C diagnosis in relation to disease decompensation and hepatocellular carcinoma development. J Hepatol. 2017;67:909–917. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.06.025. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
