Can Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Predict Various Levels of Echelon Nodes in Oral Cancers?
- PMID: 32256831
- PMCID: PMC6828571
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1695762
Can Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Predict Various Levels of Echelon Nodes in Oral Cancers?
Abstract
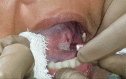
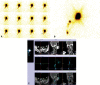
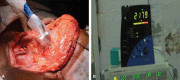
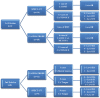
Introduction The efficacy of sentinel node biopsy in early stage oral cancer is well established. Its evolving role can be reinforced by further studies. Objective Analyzing the predictability of the levels of echelon nodes for various oral cavity tumor subsites on sentinel node biopsy. Methods A prospective study of 20 patients with stage I/II oral squamous cell carcinoma who underwent sentinel node biopsy-guided neck dissection between January 2017 and 2018 at our institute. The procedure included radiotracer injection, imaging (lymphoscintigraphy, single photon emission computed tomography-computed tomography), and gamma probe application. Sentinel node detection on imaging and gamma probe were compared. Results Out of 20 patients, 13 (65%) had carcinoma of the tongue, 6 (30%) had buccal mucosa carcinoma, and 1 (5%) had retromolar trigone carcinoma. The mean age of the patients was 52.3 years. A total of 13 (65%) patients were male, and 7 (35%) were female. The sentinel node identification rates with imaging and gamma probe were of 70% and 100% respectively. In tongue and retromolar trigone primaries, the most common first-echelon nodes in both modalities were levels IIA and IB respectively. For buccal mucosa primaries, first-echelon nodes were detected only with the gamma probe, which was level IB. On imaging, second-echelon nodes were detected only for tongue primaries, and had equivalent incidence of levels II, III, and IV. On the gamma probe, level IIA, followed by III, and IV for the tongue, and level IIA were the most common second-echelon nodes for the buccal mucosa. Third-echelon nodes were detected only with the gamma probe for tongue carcinoma at level IV. Conclusion The combined use of imaging and gamma probe provides the best results, with high identification rate and predictability of echelon levels.
Keywords: lymphoscintigraphy; neck dissection; oral cancer; sentinel node; technetium.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors have none to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SPECT-CT for topographic mapping of sentinel lymph nodes prior to gamma probe-guided biopsy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2004 Dec;32(6):343-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2004.05.008. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15555515
-
Comparison between one day and two days protocols for sentinel node mapping of breast cancer patients.Hell J Nucl Med. 2011 Sep-Dec;14(3):313-5. Hell J Nucl Med. 2011. PMID: 22087458
-
[Application value of sentinel node biopsy in early stage oral tongue cancer with clinically negative neck].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013 Jun;35(6):459-62. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24119908 Chinese.
-
The application of sentinel node radiolocalization to solid tumors of the head and neck: a 10-year experience.Laryngoscope. 2004 Jan;114(1):2-19. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200401000-00002. Laryngoscope. 2004. PMID: 14709988 Review.
-
Role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in oral cancer.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2006 Dec;26(6):345-9. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2006. PMID: 17633153 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pretreatment Blood Markers in the Prediction of Occult Neck Metastasis: A 10-Year Retrospective Study.Cureus. 2021 Jul 26;13(7):e16641. doi: 10.7759/cureus.16641. eCollection 2021 Jul. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34458043 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Oral Biopsies, Sample Types, and Detection Techniques Applied in Relation to Oral Cancer Detection.BioTech (Basel). 2022 Mar 2;11(1):5. doi: 10.3390/biotech11010005. BioTech (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35822813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Woolgar J A. Detailed topography of cervical lymph-node metastases from oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;26(01):3–9. - PubMed
-
- Nieweg O E, Tanis P J, Kroon B B. The definition of a sentinel node. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8(06):538–541. - PubMed
-
- Ziessman H A, O'Malley J P, Thrall J H, Fahey F H.Oncology: Non-positron emission tomography. Nuclear medicine-the requisitesIn:, editors.Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 2014281–283.
-
- Bluemel C, Herrmann K, Giammarile F et al.EANM practice guidelines for lymphoscintigraphy and sentinel lymph node biopsy in melanoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42(11):1750–1766. - PubMed
-
- Ziessman H A, O'Malley J P, Thrall J H, Fahey F H.Radiation detection and instrumentation. Nuclear medicine-the requisitesIn:, editors.Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 201442–44.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

