Is there any link between vitamin D deficiency and vasovagal syncope?
- PMID: 32256891
- PMCID: PMC7132194
- DOI: 10.1002/joa3.12309
Is there any link between vitamin D deficiency and vasovagal syncope?
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate serum 25[OH]D levels between patients with vasovagal syncope (VVS) diagnosed with head-up tilt table test (HUTT) and age-matched healthy people.
Methods: The study included 75 consecutive patients (32.3 ± 10.7 years), who presented with syncope and underwent HUTT and 52 healthy controls (32.9 ± 14.1 years). HUTT patients were divided into two groups according to whether there was syncope response to the test. Patients underwent cardiac, psychiatric, and neurological investigation. Serum 25[OH]D levels were measured by chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay method.
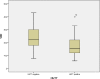
Results: There was no difference between the two groups in terms of age, gender, body mass index (BMI), echocardiographic findings (P > .05). Mean serum 25[OH]D (24.5 ± 6.3 vs 20.1 ± 8.8 ng/mL, P = .003) and vitamin B12 levels (436.4 ± 199.2 vs 363.1 ± 107.6 pg/mL, P = .009) was lower in syncope patients when compared to the control group. In correlation analyses, syncope was shown as correlated with the vitamin D (r = -264, P = .003) and vitamin B12 levels (r = -233, P = .009). But, multivariate regression analyses showed that only vitamin D increased risk of syncope [OR: 0.946, 95% CI (0.901-0.994)]. There was no difference in terms of age, gender, BMI, echocardiographic findings between the in HUTT positive (n = 45) and negative groups (n = 29). Only vitamin D level was significantly lower in HUTT positive group (17.5 ± 7.7 vs 24.4 ± 9.1 ng/mL, P = .002). There was no difference among in the vasovagal subgroups in terms of vitamin D level and other features.
Conclusion: Vitamin D and B12 levels were reasonably low in syncope patients, but especially low Vitamin D levels were associated with VVS diagnosed in HUTT.
Keywords: head‐up tilt table test; syncope; vitamin D deficiency.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Arrhythmia published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of the Japanese Heart Rhythm Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interests for this article. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients before participating in the study
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Association of vitamin D deficiency with severity of symptoms in children with vasovagal syncope].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Jun 2;60(6):557-561. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20211009-00854. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35658362 Chinese.
-
The effects of ALDH2 Glu487Lys polymorphism on vasovagal syncope patients undergoing head-up tilt test supplemented with sublingual nitroglycerin.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Oct 28;22(1):451. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02901-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 36307771 Free PMC article.
-
Age Is a Predictor for the Syncope Recurrence in Elderly Vasovagal Syncope Patients With a Positive Head-Up Tilt Test.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jun 29;8:667171. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.667171. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34268342 Free PMC article.
-
The benefit of closed loop stimulation in patients with cardioinhibitory vasovagal syncope confirmed by head-up tilt table testing: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2019 Jun;55(1):105-113. doi: 10.1007/s10840-019-00531-0. Epub 2019 Mar 12. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30863907
-
Pacing for vasovagal syncope: Tips for use in practice.Auton Neurosci. 2022 Sep;241:102998. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2022.102998. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Auton Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35696879 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D Deficiency and Vasovagal Syncope in Children and Adolescents.Front Pediatr. 2021 Feb 25;9:575923. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.575923. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33732666 Free PMC article.
-
Energy metabolism and syncope.Clin Auton Res. 2022 Dec;32(6):391-393. doi: 10.1007/s10286-022-00906-w. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Clin Auton Res. 2022. PMID: 36326945 No abstract available.
-
Vitamin D Deficiency in Children With Vasovagal Syncope Is Associated With Impaired Circadian Rhythm of Blood Pressure.Front Neurosci. 2021 Aug 12;15:712462. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.712462. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34456677 Free PMC article.
-
Association between vitamin D deficiency and vasovagal syncope: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Cardiol. 2023 Jul;46(7):721-728. doi: 10.1002/clc.24035. Epub 2023 May 24. Clin Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37226313 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Vitamin D Levels in Children and Adolescents with Vasovagal Syncope, Syncope Due to Orthostatic Hypotension, and Cardiac Syncope.Turk Arch Pediatr. 2023 Jan;58(1):42-48. doi: 10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2022.22141. Turk Arch Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36598210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shen W‐K, Sheldon RS, Benditt DG, Cohen MI, Forman DE, Goldberger ZD, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for the evaluation and management of patients with syncope: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2017;136:65–77. - PubMed
-
- Del Rosso A, Alboni P, Brignole M, Menozzi C, Raviele A. Relation of clinical presentation of syncope to the age of patients. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96:1431–5. - PubMed
-
- Calkins H, Zipes DP. Hypotension and syncope In: Robert O, Bonow MD, Douglas L, Mann MD, Douglas P, Zipes MD, Peter Libby MD, editors. Braunwald's heart disease. Philadelphia PA: Elsevier Saunders; 8th ed 2008; p. 975–83.
-
- Soteriades ES, Evans JC, Larson MG, Chen MH, Chen L, Benjamin EJ, et al. Insidans and prognosis of syncope. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:878–85. - PubMed
-
- Duygu H, Zoghi M, Turk U, Akyuz S, Ozerkan F, Akilli A, et al. The role of tilt training in preventing recurrent syncope in patients with vasovagal syncope: a prospective and randomised study. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2008;31:592–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources