Effect of Caesalpinia bonduc Polyphenol Extract on Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats in Attenuating Hyperglycemia by Upregulating Insulin Secretion and Inhibiting JNK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 32256963
- PMCID: PMC7103044
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9020219
Effect of Caesalpinia bonduc Polyphenol Extract on Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats in Attenuating Hyperglycemia by Upregulating Insulin Secretion and Inhibiting JNK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
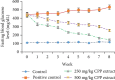
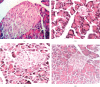
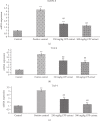
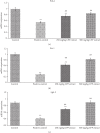
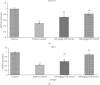
Caesalpinia bonduc has been used in herbal medicines for the treatment of a wide range of diseases from decades. The present study has explored the remedial potential and underlying mechanism of polyphenol extract of Caesalpinia bonduc in alloxanized diabetic rats. HPLC/MS analysis confirmed the presence of phenolics in considerable concentrations in Caesalpinia bonduc extract. Administration of different doses (250 and 500 mg/kg) of CPP extract to hyperglycemic rats for 8 weeks restored blood and serum glucose, insulin, glycosylated hemoglobin, leptin, amylin, and carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes level towards normal compared to alloxanized diabetic group. The effect of CPP extract on various genes such as Pdx-1, Ins-1, ngn-3, GLUT-4, and IRS-1 in insulin signaling pathway and Traf-4, Traf-6, and Mapk-8 in MAPK downstream JNK cascade was examined through qRT-PCR to access the core molecular mechanism involved in CPP-induced recovery of diabetes. Results have revealed that CPP extract reduced oxidative stress in pancreatic β cells by restoring free radical scavenging potential, reducing the mRNA expression of Mapk-8, Traf-4, and Traf-6, and increasing the Pdx-1, Ins-1, ngn-3, GLUT-4, and IRS-1 expression ensuing regeneration of β cells and subsequent insulin release from pancreas. The results obtained in this study recommend that CPP extract may be a promising therapeutic restorative agent in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2020 Asra Iftikhar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alsharidah M., Algeffari M., Abdel-Moneim A. M. H., Lutfi M. F., Alshelowi H. Effect of combined gliclazide/metformin treatment on oxidative stress, lipid profile, and hepatorenal functions in type 2 diabetic patients. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2018;26(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2017.11.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

