Roscovitine enhances all- trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced nuclear enrichment of an ensemble of activated signaling molecules and augments ATRA-induced myeloid cell differentiation
- PMID: 32256976
- PMCID: PMC7105165
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.27508
Roscovitine enhances all- trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced nuclear enrichment of an ensemble of activated signaling molecules and augments ATRA-induced myeloid cell differentiation
Abstract
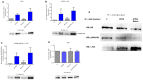
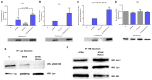
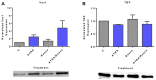
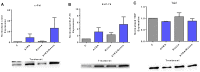
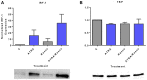
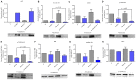
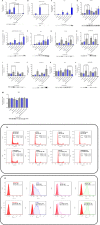
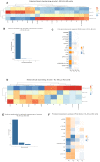
Although ATRA represents a successful differentiation therapy for APL, it is largely ineffective for non-APL AMLs. Hence combination therapies using an agent targeting ATRA-regulated molecules that drive cell differentiation/arrest are of interest. Using the HL-60 human non-APL AML model where ATRA causes nuclear enrichment of c-Raf that drives differentiation/G0-arrest, we now observe that roscovitine enhanced nuclear enrichment of certain traditionally cytoplasmic signaling molecules and enhanced differentiation and cell cycle arrest. Roscovitine upregulated ATRA-induced nuclear c-Raf phosphorylation at S259 and S289/296/301. Nuclear c-Raf interacted with RB protein and specifically with pS608RB, the hinge region phosphorylation controlling E2F binding and cell cycle progression. ATRA-induced loss of pS608RB with cell cycle arrest was associated with loss of RB-sequestered c-Raf, thereby coupling cell cycle arrest and increased availability of c-Raf to promote differentiation. Part of this mechanism reflects promoting cell cycle arrest via ATRA-induced upregulation of the p27 Kip1 CDKI. Roscovitine also enhanced the ATRA-induced nuclear enrichment of other signaling molecules traditionally perceived as cytoplasmic promoters of proliferation, but now known to promote differentiation; in particular: SFKs, Lyn, Fgr; adaptor proteins, c-Cbl, SLP-76; a guanine exchange factor, Vav1; and a transcription factor, IRF-1. Akin to c-Raf, Lyn bound to RB, specifically to pS608RB. Lyn-pS608RB association was greatly diminished by ATRA and essentially lost in ATRA plus roscovitine treated cells. Interestingly Lyn-KD enhanced such ATRA-induced nuclear signaling and differentiation and made roscovitine more effective. ATRA thus mobilized traditionally cytoplasmic signaling molecules to the nucleus where they drove differentiation which were further enhanced by roscovitine.
Keywords: APL; ATRA; HL-60; Lyn; roscovitine.
Copyright: © 2020 Rashid et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roscovitine enhances All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced leukemia cell differentiation: Novel effects on signaling molecules for a putative Cdk2 inhibitor.Cell Signal. 2020 Jul;71:109555. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109555. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32032659
-
Dissecting the novel partners of nuclear c-Raf and its role in all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced myeloblastic leukemia cells differentiation.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Sep 1;394(1):111989. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111989. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32283065 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of c-Cbl and p85 PI3K driven by all-trans retinoic acid and CD38 depends on Lyn kinase activity.Cell Signal. 2014 Jul;26(7):1589-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.03.021. Epub 2014 Mar 29. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24686085 Free PMC article.
-
All-trans retinoic acid and hematopoietic growth factors regulating the growth and differentiation of blast progenitors in acute promyelocytic leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 1999 Apr;33(3-4):267-80. doi: 10.3109/10428199909058426. Leuk Lymphoma. 1999. PMID: 10221506 Review.
-
Reprogramming acute myeloid leukemia into sensitivity for retinoic-acid-driven differentiation.Exp Hematol. 2017 Aug;52:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Exp Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28456748 Review.
Cited by
-
Role for Fgr and Numb in retinoic acid-induced differentiation and G0 arrest of non-APL AML cells.Oncotarget. 2021 Jun 8;12(12):1147-1164. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27969. eCollection 2021 Jun 8. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 34136084 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptors in health and disease: signaling pathways, biological functions and pharmaceutical interventions.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jul 28;10(1):228. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02270-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40717128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of midostaurin and ATRA exerts dose-dependent dual effects on acute myeloid leukemia cells with wild type FLT3.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jul 9;22(1):749. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09828-2. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35810308 Free PMC article.
-
FGR Src family kinase causes signaling and phenotypic shift mimicking retinoic acid-induced differentiation of leukemic cells.Oncotarget. 2025 Mar 21;16:202-218. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28705. Oncotarget. 2025. PMID: 40116400 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Assessment of the Role of p53 on Chemotherapy Treatments in Neuroblastoma Cell Lines.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Nov 19;14(11):1184. doi: 10.3390/ph14111184. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lo-Coco F, Avvisati G, Vignetti M, Thiede C, Orlando SM, Iacobelli S, Ferrara F, Fazi P, Cicconi L, Di Bona E, Specchia G, Sica S, Divona M, et al. , and Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche dell’Adulto, and German-Austrian Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group, and Study Alliance Leukemia . Retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:111–21. 10.1056/NEJMoa1300874. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

