Automated imaging cytometry reveals dysplastic indices of colonic serrated adenomas
- PMID: 32257372
- PMCID: PMC7117562
- DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2019-0111
Automated imaging cytometry reveals dysplastic indices of colonic serrated adenomas
Abstract
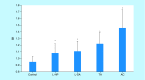
Aim: Left-sided colonic serrated adenomas (L-SAs) were evaluated for aneuploidy using automated imaging cytometry to quantify DNA content and compared with normal colonic tissues (NCT), tubular adenomas (TA), left-sided hyperplastic polyps (L-HP) and adenocarcinomas.
Materials & methods: We used standard paraffin-embedded Feulgen-stained tissue sections.
Results: The mean DNA index (DI) of NCT was 0.95, L-HP was 1.08, TA was 1.22, L-SA was 1.11 and adenocarcinomas was 1.46. DI of L-SA was statistically higher than that of NCT, but not statistically different from L-HP.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that DIs correlate with the described neoplastic progression of L-SA, TA and L-SA compared with NCT and suggests that L-SA may be involved in a chromosome instability pathway of neoplastic progression.
Keywords: Feulgen stain; colon polyps; dysplasia; image cytometry; serrated adenoma.
© 2020 Hiroshi Mashimo.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial & competing interests disclosure The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Key statistics for colorectal cancer (2019). www.cancer.org/cancer/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
-
- Cancer facts and figures – 2017 (2019). www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures...
-
- Winawer S, Fletcher R, Rex D. et al. Colorectal cancer screening and surveillance: clinical guidelines and rationale – update based on new evidence. Gastroenterology 124(2), 544–560 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Sharma P, Bansal A. Toward better imaging of Barrett’s esophagus – see more, biopsy less! Gastrointest. Endosc. 64(2), 188–192 (2006). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
