The Effects of Salt and Glucose Intake on Angiotensin II and Aldosterone in Obese and Nonobese Patients with Essential Hypertension
- PMID: 32257423
- PMCID: PMC7106922
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6017105
The Effects of Salt and Glucose Intake on Angiotensin II and Aldosterone in Obese and Nonobese Patients with Essential Hypertension
Abstract
Background: The exact mechanisms for the development of essential hypertension are not known. Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) in adipose tissue may represent an important link between obesity and hypertension. This study investigates the effects of oral intake of glucose with and without NaCl on angiotensin II (AngII) and aldosterone in obese and nonobese patients with essential hypertension.
Methods: Twenty newly diagnosed untreated essential hypertensive patients and 15 normotensive control subjects matched for age, gender, and BMI were studied. Participants fasted overnight (8-10 hrs), and then each subject took 75 gm glucose alone and with 3 gm NaCl, each dissolved in 250 ml. Subjects were monitored for 2 hours. Half hourly BP, plasma glucose (PG), serum Na+, K+, insulin, AngII, and aldosterone were measured. Subjects were classified into obese (BMI >30 Kg/m2) (11 patients and 8 control) and nonobese (BMI <30 Kg/m2) (9 patients and 7 control).
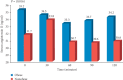
Results: After intake of glucose with NaCl serum, AngII was significantly higher in obese hypertensive patients compared with nonobese patients (P = 0.016). Intake of glucose with NaCl resulted in a significantly higher serum Na in obese hypertensive patients compared with nonobese patients Na (P = 0.009). Serum aldosterone was significantly higher in obese patients (P = 0.03, after glucose; P = 0.003, after glucose with NaCl) and in nonobese patients (P = 0.000 and P = 0.000, respectively) compared with their respective normotensive control subjects. In obese and nonobese patients, intake of glucose and glucose with NaCl showed no significant change in the levels of serum AngII and aldosterone which was associated a significant increase in serum Na in obese patients (P = 0.03) and a highly significant reduction in serum K in nonobese patients (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Failure of suppression or inappropriate maintenance of secretion of AngII and aldosterone in both hypertensive groups by intake of glucose with NaCl may indicate a possible mechanism of essential hypertension.
Copyright © 2020 Nouralsalhin Alaagib et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The state and responsiveness of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in patients with type II diabetes mellitus.Am J Hypertens. 1999 Apr;12(4 Pt 1):348-55. Am J Hypertens. 1999. PMID: 10232494 Clinical Trial.
-
Relation between the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and left ventricular structure and function in young normotensive and mildly hypertensive subjects.Am Heart J. 1999 Nov;138(5 Pt 1):810-7. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(99)70004-9. Am Heart J. 1999. PMID: 10539810
-
Increased aldosterone/renin quotient in obese hypertensive women: a novel role for low-density lipoproteins?Horm Metab Res. 2006 Jul;38(7):471-5. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-948137. Horm Metab Res. 2006. PMID: 16933186
-
The pathogenesis of hypertension in obese subjects.Drugs. 1993;46 Suppl 2:197-208; discussion 208-9. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199300462-00030. Drugs. 1993. PMID: 7512475 Review.
-
Dysregulation of blood pressure in normotensive offspring of hypertensive parents.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12 Suppl 3:S134-48. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988. PMID: 2467099 Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship between adipose tissue RAAS activity and the risk factors of prediabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Adipocyte. 2023 Dec;12(1):2249763. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2023.2249763. Adipocyte. 2023. PMID: 37606270 Free PMC article.
-
Role of skeletal muscle perfusion and insulin resistance in the effect of dietary sodium on heart function in overweight.ESC Heart Fail. 2021 Dec;8(6):5304-5315. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13620. Epub 2021 Sep 22. ESC Heart Fail. 2021. PMID: 34551207 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Poor Performance of Angiotensin II Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assays in Mostly Hypertensive Cohort Routinely Screened for Primary Aldosteronism.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;12(5):1124. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051124. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626280 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: From Childhood to Adulthood.Nutrients. 2021 Nov 22;13(11):4176. doi: 10.3390/nu13114176. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity, Sodium Homeostasis, and Arterial Hypertension in Children and Adolescents.Nutrients. 2021 Nov 11;13(11):4032. doi: 10.3390/nu13114032. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836287 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources