COVID-19 infection: Origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses
- PMID: 32257431
- PMCID: PMC7113610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.005
COVID-19 infection: Origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses
Abstract
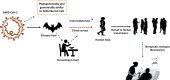
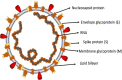
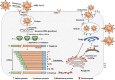
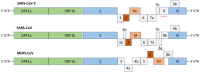
The coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is a highly transmittable and pathogenic viral infection caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which emerged in Wuhan, China and spread around the world. Genomic analysis revealed that SARS-CoV-2 is phylogenetically related to severe acute respiratory syndrome-like (SARS-like) bat viruses, therefore bats could be the possible primary reservoir. The intermediate source of origin and transfer to humans is not known, however, the rapid human to human transfer has been confirmed widely. There is no clinically approved antiviral drug or vaccine available to be used against COVID-19. However, few broad-spectrum antiviral drugs have been evaluated against COVID-19 in clinical trials, resulted in clinical recovery. In the current review, we summarize and comparatively analyze the emergence and pathogenicity of COVID-19 infection and previous human coronaviruses severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). We also discuss the approaches for developing effective vaccines and therapeutic combinations to cope with this viral outbreak.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronaviruses; Origin; Outbreak; Spread.
© 2020 THE AUTHORS. Published by Elsevier BV on behalf of Cairo University.
Figures


References
-
- Organization WH. Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in suspected human cases: interim guidance, 2 March 2020. World Health Organization, 2020.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

