Etoricoxib prevents progression of osteolysis in repeated intra-articular monosodium urate-induced gouty arthritis in rats
- PMID: 32257433
- PMCID: PMC7114632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.02.014
Etoricoxib prevents progression of osteolysis in repeated intra-articular monosodium urate-induced gouty arthritis in rats
Abstract
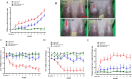
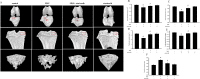
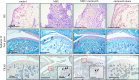
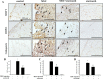
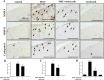
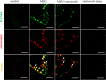
Deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in the joint or synovium is the major factor in Gouty arthritis (GA). The clinical features of chronic and recurrent GA include pain and the subsequent development of chronic tophaceous GA with multiple tophi deposits accompanied by osteolysis. The majority of previous animal studies have focused on MSU-induced acute GA without making observations regarding osteolysis. In the study, intra-articular injections of MSU into the knee (2 times/week for 10 weeks) was used to induce chronic and recurrent attacks of GA that in turn induced progressive osteolysis. Moreover, we also evaluated whether the clinical, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) etoricoxib attenuated the osteoclastogenesis of progressive osteolysis. The knee morphometry and the expression of osteoclastogenesis-related proteins (cathepsin K and matrix metalloproteinase-9 and -13) in the knee were examined by micro-CT and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Results showed that oral etoricoxib not only significantly attenuated the nociceptive behaviors of the rats but that it also inhibited the expression of osteoclastogenesis-related proteins in their knee joints in chronic and recurrent attacks of GA. Our findings thus suggest that NSAIDs not only inhibit nociception but also prevent the progression of osteolysis in chronic and repeated attacks of GA.
Keywords: Chronic, recurrent gouty arthritis; Micro-CT; Osteoclastogenesis; Rat model.
© 2020 THE AUTHORS. Published by Elsevier BV on behalf of Cairo University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Sundy J.S., Baraf H.S., Yood R.A., Edwards N.L., Gutierrez-Urena S.R., Treadwell E.L. Efficacy and tolerability of pegloticase for the treatment of chronic gout in patients refractory to conventional treatment: two randomized controlled trials. JAMA. 2011;306:711–720. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

