Ketogenic Diet Ameliorates Cardiac Dysfunction via Balancing Mitochondrial Dynamics and Inhibiting Apoptosis in Type 2 Diabetic Mice
- PMID: 32257538
- PMCID: PMC7069456
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2019.0510
Ketogenic Diet Ameliorates Cardiac Dysfunction via Balancing Mitochondrial Dynamics and Inhibiting Apoptosis in Type 2 Diabetic Mice
Abstract
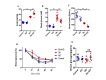
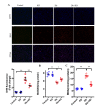
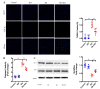
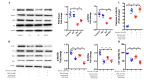
The ketogenic diet (KD) has been widely used in clinical studies and shown to hace an anti-diabetic effect, but the underlying mechanisms have not been fully elaborated. Our aim was to investigate the effects and the underling mechanisms of the KD on cardiac function in db/db mice. In the present study, db/db mice were subjected to a normal diet (ND) or KD. Fasting blood glucose, cardiac function and morphology, mitochondrial dynamics, oxidative stress, and apoptosis were measured 8 weeks post KD treatment. Compared with the ND, the KD improved glycemic control and protected against diabetic cardiomyopathy in db/db mice, and improved mitochondrial function, as well as reduced oxidative stress were observed in hearts. In addition, KD treatment exerted an anti-apoptotic effect in the heart of db/db mice. Further data showed that the PI3K/Akt pathway was involved in this protective effect. Our data demonstrated that KD treatment ameliorates cardiac dysfunction by inhibiting apoptosis via activating the PI3K-Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic mice, suggesting that the KD is a promising lifestyle intervention to protect against diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: db/db mice; diabetic cardiomyopathy; ketogenic diet; lifestyle intervention.
Copyright: © 2020 Guo et al.
Figures


References
-
- Wallia A and Molitch ME (2014). Insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA, 311: 2315-25. - PubMed
-
- Joubert M, Manrique A, Cariou B, Prieur X (2018). Diabetes-related cardiomyopathy: The sweet story of glucose overload from epidemiology to cellular pathways. Diabetes Metab. - PubMed
-
- Fein FS, Cho S, Malhotra A, Akella J, VanHoeven KH, Sonnenblick EH, et al. (1991). Beneficial effects of diltiazem on the natural history of hypertensive diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. J Am Coll Cardiol, 18: 1406-17. - PubMed
-
- Fein FS (1990). Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Care, 13: 1169-79. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
