Oral ethinyl estradiol treatment in women with cystic fibrosis is associated with lower bone mineral density
- PMID: 32257821
- PMCID: PMC7109452
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcte.2020.100223
Oral ethinyl estradiol treatment in women with cystic fibrosis is associated with lower bone mineral density
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to determine whether estrogen supplementation primarily from oral contraceptive pills compared to no estrogen supplementation is associated with differences in mean bone mineral density (BMD) measured by DXA in a cross-sectional study of women with cystic fibrosis (CF).
Methods: In this cross-sectional study of women with CF followed at a single center, we analyzed 49 women with CF ages 18-50 years with a documented DXA. BMD of women with CF taking estrogen supplementation was compared to BMD of women with CF not taking estrogen supplementation.
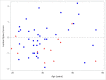
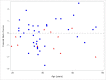
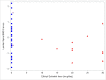
Results: Twelve women with CF were taking estrogen supplementation with mean dose of 23.3 mcg/day (SD 6.9 mcg/day) of ethinyl estradiol. There were no statistically significant differences between demographics of the 12 women with CF taking estrogen supplementation compared to the 37 women with CF not taking estrogen supplementation. Women taking estrogen had lower mean lumbar spine Z-score: -0.7 ± 0.7, compared to women not taking estrogen, Z-score: -0.04 ± 1.0 (p-value 0.046). Women taking estrogen had lower mean BMD at the lumbar spine: 0.952 ± 0.086 g/cm2, compared to women not taking estrogen: 1.023 ± 0.105 g/cm2 (p-value 0.038). Similar trends were seen at the total hip and femoral neck.
Conclusion: Low-dose estrogen supplementation in premenopausal women with CF was associated with lower BMD compared to no estrogen supplementation in a similar group of premenopausal young women with CF. Future studies are needed to investigate the optimal formulation, route of administration, and dose to accrue and preserve bone mass in premenopausal women with CF.
Keywords: BMD, Bone mineral density; BMI, Body mass index; CF, Cystic fibrosis; CFBD, Cystic fibrosis-related bone disease; CFTR, Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; Cystic fibrosis-related bone disease; DXA, Dual X-ray absorptiometry; Estrogen; Ethinyl estradiol; FEV1, Forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC, Forced vital capacity; Hypogonadism; Lumbar spine; Osteoporosis; POI, Primary ovarian insufficiency.
Figures


References
-
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Patient Registry 2018 Annual Data Report. Bethesda, Maryland: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation; 2019.
-
- Sermet-Gaudelus I., Bianchi M.L., Garabedian M. European cystic fibrosis bone mineralisation guidelines. J Cyst Fibros. 2011;10(Suppl 2):S16–S23. - PubMed
-
- Aris R.M., Merkel P.A., Bachrach L.K. Guide to bone health and disease in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:1888–1896. - PubMed
-
- Putman M.S., Anabtawi A., Le T., Tangpricha V., Sermet-Gaudelus I. Cystic fibrosis bone disease treatment: current knowledge and future directions. J Cyst Fibros. 2019;18:S56–S65. - PubMed
-
- Umlawska W., Sands D., Zielinska A. Age of menarche in girls with cystic fibrosis. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2010;48:185–190. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

